Dapagliflozin vs empagliflozin in patients with chronic heart failure: a registry analysis
- PMID: 40343436
- PMCID: PMC12093124
- DOI: 10.3325/cmj.2025.66.135
Dapagliflozin vs empagliflozin in patients with chronic heart failure: a registry analysis
Abstract
Aim: To assess the relative efficacy of dapagliflozin and empagliflozin in routinely treated chronic heart failure (CHF) patients.
Methods: Data from a registry of prevalent and incident CHF patients were used to set up cohorts (new-user design) of patients started on dapagliflozin or empagliflozin in addition to other guideline-directed therapy. Cohorts were mutually balanced on a range of characteristics, and were assessed for the incidence of a composite of all-cause death/major adverse cardiac events (primary outcome) over the initial 6 months of treatment, and for New York Heart Association (NYHA) functional class at 6 months (secondary outcome). Frequentist and Bayes estimates were generated for the dapagliflozin vs empagliflozin comparison.
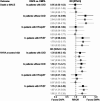
Results: In both prevalent (dapagliflozin n=393, empagliflozin n=328) and incident (dapagliflozin n=124, empagliflozin n=116) patients, those prescribed dapagliflozin had somewhat higher incidence of the primary outcome, but the confidence intervals were wide (RR=1.385, 95%CI 0.882-2.173 [prevalent], RR=2.192, 95%CI 0.765-6.282 [incident]), and were more likely to present with a worse NYHA class at 6 months (OR=1.552, 95%CI 1.142-2.108 [prevalent], OR=1.503, 95%CI 0.844-2.676 [incident]). In the pooled data, primary events (n=102) were more common in dapagliflozin-prescribed patients (frequentist estimate RR=1.519, 95%CI 1.239-1.861; Bayes RR=1.380, 95%CrI 0.981-1.944). Dapagliflozin-prescribed patients were also more likely to have a worse NYHA class at 6 months (OR=1.540, 95%CI 1.208-1.962; Bayes OR=1.425, 95%CrI 1.098-1.781).
Conclusion: CHF patients prescribed with dapagliflozin had poorer outcomes than their empagliflozin-prescribed peers over the initial 6 months of treatment. Data emphasize a need for a direct randomized comparison of the two treatments in this setting.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

