Extracellular PKM2 modulates cancer immunity by regulating macrophage polarity
- PMID: 40343475
- PMCID: PMC12064527
- DOI: 10.1007/s00262-025-04050-y
Extracellular PKM2 modulates cancer immunity by regulating macrophage polarity
Abstract
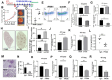
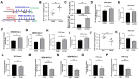
Tumor controls its immunity by educating its microenvironment, including regulating polarity of tumor associated macrophages. It is well documented that cancer cells release PKM2 to facilitate tumor progression. We report here that the extracellular PKM2 (EcPKM2) modulates tumor immunity by facilitating M2 macrophage polarization in tumors. EcPKM2 interacts with integrin αvβ3 on macrophage to activate integrin-FAK-PI3K signal axis. Activation of FAK-PI3K by EcPKM2 suppresses PTEN expression, which subsequently upregulates arginase1 (Arg1) expression and activity in macrophage to facilitate M2 polarity. Our studies uncover a novel and important mechanism for modulation of tumor immunity. More importantly, an antibody against PKM2 that disrupts the interaction between EcPKM2 and integrin αvβ3 is effective in converting M2 macrophages to M1 macrophages in tumors, suggesting a new therapeutic strategy and target for cancer therapies. Combination of the anti-PKM2 antibody with checkpoint blockades provides enhanced treatment effects.
Keywords: Arginase1; Cancer immunotherapy; Glycolysis; Integrin αvβ3; Macrophage; Pyruvate kinase M2.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Conflict interest: The authors declare no competing conflict of interests
Figures




References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

