Phase 1 study of talquetamab, a humanized GPRC5D x CD3 bispecific antibody, in Japanese patients with relapsed/refractory MM
- PMID: 40343678
- PMCID: PMC12380926
- DOI: 10.1007/s12185-025-03991-5
Phase 1 study of talquetamab, a humanized GPRC5D x CD3 bispecific antibody, in Japanese patients with relapsed/refractory MM
Abstract
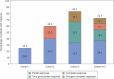
The bispecific antibody talquetamab demonstrated substantial responses in heavily pretreated relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma (RRMM) in the global phase 1/2 MonumenTAL-1 study. This study, evaluated the safety and efficacy of talquetamab in Japanese patients with RRMM pretreated with a proteasome inhibitor, immunomodulatory drug, and anti-CD38 monoclonal antibody. The primary endpoints were frequency and type of treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs) and serious AEs including dose-limiting toxicity (DLT). The secondary endpoints were overall response (ORR; partial response or better), duration of, and time to response. At data cutoff, 15 patients had received subcutaneous talquetamab at three doses (Cohort 1: 135 µg/kg weekly [QW, n = 4]; Cohort 2: 400 µg/kg [QW, n = 5]; Cohort 3: 800 µg/kg [Q2W, n = 6]). No DLTs, deaths, or AE-related dose reductions/treatment discontinuation were observed. Common TEAEs were neutropenia (60.0%), lymphopenia (53.3%), and CRS (46.7%). TEAEs of clinical interest (all Grade ≤ 2) were dysgeusia, skin toxicity, nail disorder, and dry mouth. With an overall median follow-up of 9.0 months, the ORR was 60.0% (95% confidence interval 32.3%, 83.7%). Talquetamab showed substantial responses in Japanese patients with RRMM, consistent with the global MonumenTAL-1 study, supporting its potential as a new standard of care for Japanese RRMM patients.
Keywords: Immunotherapy; Japanese population; Relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma; Talquetamab.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Conflict of interest: Shinsuke Iida: All support for the present manuscript received from Janssen. Grants received from Abbvie, Amgen, BMS, Daiichi Sankyo, GSK, Janssen, Novartis, Ono, Otsuka, Pfizer Sanofi, Shionogi, and Takeda and paid to the institution. Consulting fees received from Abbvie, Astrazeneca, BMS, GSK, Janssen, Novartis, Otsuka, Pfizer, and Sanofi. Payment or honoraria received from Astrazeneca, BMS, Janssen, Pfizer, Sanofi, and Takeda, paid to the author. Other financial or non-financial interests received from Chugai as subsidy. Kazutaka Sunami: Grants as research funding received from: Abbvie, Beigene, BMS, Chugai, GSK, Incyte, Janssen, Kyowa Kirin, Mitsubishi Tanabe, Novartis, Ono, Otsuka, Pfizer, and Sanofi. Honoraria received from BMS, Janssen, and Sanofi. Shigeki Ito: Grant or research funding received from Abbvie, BMS, GSK, Janssen, Pfizer, and Sanofi. Honoraria received from BMS, Janssen, Pfizer, Takeda and Sanofi. Junichiro Yuda: has received research funding from AbbVie, Amgen, BMS, Chugai, Daiichi Sankyo, Genmab, Incyte, Janssen, Novartis, Mitsubishi Tanabe, MSD, Sumitomo, and Takeda. Participated on a data safety monitoring board or advisory board for Janssen. Ei Fujikawa: Employee of Janssen Pharmaceutical K.K. Mikihiro Takamoto: Employee of Janssen Pharmaceutical K.K. Kensuke Aida: Employee of Janssen Pharmaceutical K.K. Hiroshi Yamazaki: Employee of Janssen Pharmaceutical K.K., own stocks or stock options in Kameya Shoji Co., Ltd. Marimo Takahashi: Employee of Janssen Pharmaceutical K.K. Owns stock or stock options in J&J innovative medicine. Tadao Ishida: Grants as Research funding received from Alexion pharma, BMS, GSK, Janssen, Pfizer, Prothena, Sanofi, and Takeda. Payment or honoraria received from BMS, CSL Behring, Janssen, Ono, Pfizer, Sanofi, and Takeda. Ethical approval: The study was conducted in accordance with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki and the International Council for Harmonization guidelines for Good Clinical Practice. The study, protocol along with any amendments, was approved by the institutional review boards at each participating study site. All patients also provided written informed consent.
Figures



References
-
- Moreau P, de Wit E. Recent progress in relapsed multiple myeloma therapy: implications for treatment decisions. Br J Haematol. 2017;179(2):198–218. 10.1111/bjh.14780. - PubMed
-
- Iida S, Ishida T, Murakami H, Ozaki S, Abe M, Hata H, et al. JSH practical guidelines for hematological malignancies, 2018: III. Myeloma-1. Multiple myeloma (MM). Int J Hematol. 2019;109(5):509–38. 10.1007/s12185-019-02636-8. - PubMed
-
- Ozaki S, Handa H, Saitoh T, Murakami H, Itagaki M, Asaoku H, et al. Evaluation of the revised international staging system (R-ISS) in Japanese patients with multiple myeloma. Ann Hematol. 2019;98(7):1703–11. 10.1007/s00277-019-03702-1. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

