Efficacy and factors influencing toric orthokeratology lenses in managing moderate to high astigmatic myopia
- PMID: 40343786
- PMCID: PMC12184966
- DOI: 10.1097/OPX.0000000000002264
Efficacy and factors influencing toric orthokeratology lenses in managing moderate to high astigmatic myopia
Abstract
Significance: Toric orthokeratology lenses show potential in slowing myopia progression in adolescents with moderate to high astigmatic myopia. These findings support the broader application of toric orthokeratology in managing challenging refractive conditions and mitigating myopia-related complications.
Purpose: This study seeks to probe the efficacy of toric orthokeratology lenses in controlling moderate to high astigmatic myopia in adolescents and to analyze the risk factors influencing treatment outcomes.
Methods: One hundred adolescent patients with moderate to high astigmatic myopia who were treated at our medical facility from January 2022 to January 2023 were randomly selected as the study subjects. All patients were allocated to either the experimental group (n = 50) or the control group (n = 50) using a random number table method. The control group was subjected to treatment with spherical orthokeratology lenses, whereas the experimental group was treated with toric orthokeratology lenses. Changes in uncorrected visual acuity, axial length, cylinder diopters, sphere diopters, and average corneal curvature before treatment and after 12 months of treatment were compared between the two groups. The logistic regression analysis was conducted to identify the factors influencing the efficacy of toric orthokeratology lenses in controlling moderate to high astigmatic myopia in adolescents.
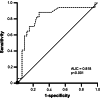
Results: Both cohorts showed substantial improvements in uncorrected visual acuity, axial length, sphere, and average corneal curvature compared with their pre-treatment values, with the experimental cohort showing greater improvements than the control cohort (p=0.01, 0.03, 0.00, 0.00). There were no significant differences in cylinder between the two groups after treatment (p=0.56). Univariate analysis unraveled significant differences in age, baseline sphere, average corneal E value, baseline axial length, and central corneal thickness (p=0.00, 0.03, 0.04, 0.02, 0.05). Receiver operating characteristic curve analysis displayed that the area under the curve for the logistic regression model attained 0.82, with a 95% confidence interval of (0.69, 0.95), sensitivity of 88%, specificity of 72%, and a Youden index of 0.61.
Conclusions: Toric orthokeratology lenses demonstrate potential efficacy for adolescents with moderate to high astigmatic myopia by slowing myopia progression. Patients who are older, severely nearsighted, and have longer baseline axial length experience more significant control over myopia progression.
Copyright © 2025 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. on behalf of the American Academy of Optometry.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest Disclosure: None of the authors have reported a financial conflict of interest.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources