Long-Term Survival and Prognostic Factors of Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy Following Transarterial Chemoembolization for Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- PMID: 40344523
- PMCID: PMC12062511
- DOI: 10.1002/cnr2.70212
Long-Term Survival and Prognostic Factors of Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy Following Transarterial Chemoembolization for Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Abstract
Background/aims: This study presents a detailed analysis of long-term survival and critical factors influencing the outcomes of hepatocellular carcinoma patients treated with stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) and transarterial chemoembolization (TACE). Our findings provide reassurance about the potential of the combination of TACE and SBRT as an effective treatment strategy for patients with large liver tumors due to HCC.
Methods: A prospective study was conducted on 42 patients with intermediate-stage hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) at 108 Military Central Hospital between December 2018 and June 2024. Following a single session of TACE, each patient underwent SBRT 1 month later. The SBRT dose ranged from 27.5 to 48 Gy, delivered in 3-5 fractions. The patient survival analysis was conducted using the Kaplan-Meier method while examining prognostic factors influencing survival, which involved log-rank tests and Cox proportional hazards regression analysis.
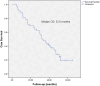
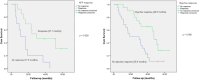
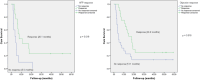
Results: Among the 42 patients (83.3% male), 34 patients (81.0%) had tumors measuring ≥ 5 cm. The median follow-up period was 32.2 months (4.5-65.1 months). The median overall survival (OS) was 32.6 months, with the respective 1-, 3-, and 5-year OS rates reported as 73.8%, 24.5%, and 19.6%. Furthermore, the median progression-free survival (PFS) was 16.6 months, with corresponding 1- and 3-year PFS rates of 71.4% and 19.0%. Factors linked to improved OS and PFS included AFP levels and treatment response based on Modified RECIST criteria. Additionally, multivariate analysis identified patient age, EQD2, and BED10 as significant predictors of better survival outcomes.
Conclusions: Our study provides evidence supporting the effectiveness and safety of combining TACE and SBRT as a treatment strategy for patients with large liver tumors due to HCC, instilling confidence in the future of HCC treatment. Positive prognostic factors included patient age, EQD2, and BED10.
Keywords: hepatocellular carcinoma; stereotactic body radiotherapy; transarterial chemoembolization.
© 2025 The Author(s). Cancer Reports published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Long-term survival analysis in combined transarterial embolization and stereotactic body radiation therapy versus stereotactic body radiation monotherapy for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma >5 cm.BMC Cancer. 2016 Nov 3;16(1):834. doi: 10.1186/s12885-016-2894-9. BMC Cancer. 2016. PMID: 27809890 Free PMC article.
-
Thermal Ablation Versus Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy After Transarterial Chemoembolization for Inoperable Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Propensity Score-Weighted Analysis.AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2021 Sep;217(3):691-698. doi: 10.2214/AJR.20.24117. Epub 2020 Sep 30. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2021. PMID: 32997517
-
Better survival after stereotactic body radiation therapy following transarterial chemoembolization in nonresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: A propensity score matched analysis.Surg Oncol. 2019 Mar;28:228-235. doi: 10.1016/j.suronc.2019.01.006. Epub 2019 Jan 29. Surg Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30851906
-
Prognosis of transarterial chemoembolization-sorafenib compared to transarterial chemoembolization-alone in hepatocellular carcinoma stage C: a systematic review.J Egypt Natl Canc Inst. 2024 May 27;36(1):18. doi: 10.1186/s43046-024-00224-4. J Egypt Natl Canc Inst. 2024. PMID: 38797810
-
Meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials of external-beam radiation versus transarterial chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma.Cancer. 2025 Feb 1;131(3):e35720. doi: 10.1002/cncr.35720. Cancer. 2025. PMID: 39887736
References
-
- Sung H., Ferlay J., Siegel R. L., et al., “Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries,” CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians 71, no. 3 (2021): 209–249. - PubMed
-
- Nguyen A. L. T., Nguyen H. T. T., Yee K. C., Palmer A. J., Blizzard C. L., and de Graaff B., “A Systematic Review and Narrative Synthesis of Health Economic Evaluations of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Screening Strategies,” Value in Health 24, no. 5 (2021): 733–743. - PubMed
-
- Nguyen‐Dinh S. H., Do A., Pham T. N. D., Dao D. Y., Nguy T. N., and M. S. Chen, Jr. , “High Burden of Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Viral Hepatitis in Southern and Central Vietnam: Experience of a Large Tertiary Referral Center, 2010 to 2016,” World Journal of Hepatology 10, no. 1 (2018): 116–123. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zhao H. C., Wu R. L., Liu F. B., et al., “A Retrospective Analysis of Long Term Outcomes in Patients Undergoing Hepatic Resection for Large (>5 Cm) Hepatocellular Carcinoma,” HPB: The Official Journal of the International Hepato Pancreato Biliary Association 18, no. 11 (2016): 943–949. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous