Antimicrobial Agent Trimethoprim Influences Chemical Interactions in Cystic Fibrosis Pathogens via the ham Gene Cluster
- PMID: 40344688
- PMCID: PMC12186260
- DOI: 10.1021/acschembio.4c00562
Antimicrobial Agent Trimethoprim Influences Chemical Interactions in Cystic Fibrosis Pathogens via the ham Gene Cluster
Abstract
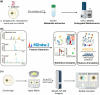
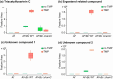
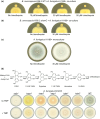
The fungus Aspergillus fumigatus and the bacterium Burkholderia cenocepacia cause fatal respiratory infections in immunocompromised humans and patients with lung disease, such as cystic fibrosis (CF). In dual infections, antagonistic interactions contribute to increased mortality. These interactions are further altered by the presence of antimicrobial and antifungal agents. However, studies performed to date on chemical interactions between clinical B. cenocepacia and A. fumigatus have focused on pathogens in isolation and do not include the most abundant chemical signal, i.e., clinically administered therapeutics, present in the lung. Here, we characterize small molecule-mediated interactions between B. cenocepacia and A. fumigatus and their shift in response to trimethoprim exposure by using metabolomics and mass spectrometry imaging. Using these methods, we report that the production of several small-molecule natural products of both the bacteria and the fungus is affected by cocultivation and exposure to trimethoprim. By systematic analysis of metabolomics data, we hypothesize that the B. cenocepacia-encoded ham gene cluster plays a role in the trimethoprim-mediated alteration of bacterial-fungal interactions. We support our findings by generating a genetically modified strain lacking the ham gene cluster and querying its interaction with A. fumigatus. Using comparative analyses of the extracts of wild-type and knockout strains, we report the inactivation of a bacterially produced antifungal compound, fragin, by A. fumigatus, which was verified by the addition of purified fragin to the A. fumigatus culture. Furthermore, we report that trimethoprim does not inhibit fungal growth, but affects the biochemical pathway for DHN-melanin biosynthesis, an important antifungal drug target, altering the pigmentation of the fungal conidia and is associated with modification of ergosterol to ergosteryl-3β-O-l-valine in coculture. This study demonstrates the impact of therapeutics on shaping microbial and fungal metabolomes, which influence interkingdom interactions and the expression of virulence factors. Our findings enhance the understanding of the complexity of chemical interactions between therapeutic compounds, bacteria, and fungi and may contribute to the development of selective treatments.
Figures





Similar articles
-
A Burkholderia cenocepacia-like environmental isolate strongly inhibits the plant fungal pathogen Zymoseptoria tritici.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2024 May 21;90(5):e0222223. doi: 10.1128/aem.02222-23. Epub 2024 Apr 16. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38624199 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Dec 22;12(12):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. PMID: 29271481 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Interventions for the eradication of meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in people with cystic fibrosis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Jul 21;7(7):CD009650. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009650.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Dec 13;12:CD009650. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009650.pub5. PMID: 30030966 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
The Heat Shock Transcription Factor HsfA Plays a Role in Membrane Lipids Biosynthesis Connecting Thermotolerance and Unsaturated Fatty Acid Metabolism in Aspergillus fumigatus.Microbiol Spectr. 2023 Jun 15;11(3):e0162723. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.01627-23. Epub 2023 May 17. Microbiol Spectr. 2023. PMID: 37195179 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Mass spectrometry-based metabolomics approaches to interrogate host-microbiome interactions in mammalian systems.Nat Prod Rep. 2025 Jun 16. doi: 10.1039/d5np00021a. Online ahead of print. Nat Prod Rep. 2025. PMID: 40521991 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

