Cancer vaccine from intracellularly gelated tumor cells functionalized with CD47 blockage and damage-associated molecular pattern exposure
- PMID: 40345180
- PMCID: PMC12147843
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xcrm.2025.102092
Cancer vaccine from intracellularly gelated tumor cells functionalized with CD47 blockage and damage-associated molecular pattern exposure
Abstract
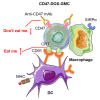
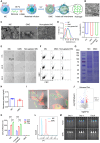
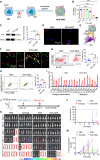
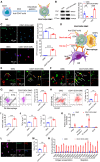
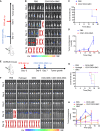
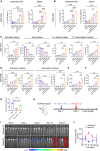
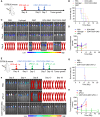
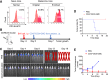
The effectiveness of whole tumor cell vaccines prepared by traditional inactivation methodology is often hindered by insufficient immunogenicity. Here, we report development of a cancer vaccine through the intracellular gelation of tumor cells, combined with CD47 blockade and damage-associated molecular pattern (DAMP) exposure, for effective tumor prevention and treatment. Intracellular hydrogelation preserves the morphology and antigenicity of tumor cells. CD47 blockade and DAMP exposure synergistically enhance the "eat me" signals and inhibit the "don't eat me" signals on tumor cells, significantly improving their immunogenicity. In the context of tumor prevention and treatment of pre-existing tumors, this vaccine polarizes CD4+ T cells toward a TH1 phenotype, reduces regulatory T cells and T cell exhaustion, and elicits a robust tumor-antigen-specific T cell response. When combined with an immune checkpoint inhibitor, this vaccine demonstrates enhanced efficacy in eradicating established tumors. The successful application of this vaccine using ascites and subcutaneous tumor cells supports the feasibility of developing personalized whole tumor cell vaccines for diverse tumor types.
Keywords: cancer treatment; hydrogel; intracellular assembly; surface engineering; tumor cell vaccine.
Copyright © 2025 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Dual blockage of both PD-L1 and CD47 enhances immunotherapy against circulating tumor cells.Sci Rep. 2019 Mar 14;9(1):4532. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-40241-1. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 30872703 Free PMC article.
-
Combining CD47 blockade with trastuzumab eliminates HER2-positive breast cancer cells and overcomes trastuzumab tolerance.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021 Jul 20;118(29):e2026849118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2026849118. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021. PMID: 34257155 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of cabazitaxel on macrophages improves CD47-targeted immunotherapy for triple-negative breast cancer.J Immunother Cancer. 2021 Mar;9(3):e002022. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2020-002022. J Immunother Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33753567 Free PMC article.
-
CD47 is a novel potent immunotherapy target in human malignancies: current studies and future promises.Future Oncol. 2018 Sep;14(21):2179-2188. doi: 10.2217/fon-2018-0035. Epub 2018 Apr 18. Future Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29667847 Review.
-
The CD47-SIRPα signaling axis as an innate immune checkpoint in cancer.Immunol Rev. 2017 Mar;276(1):145-164. doi: 10.1111/imr.12527. Immunol Rev. 2017. PMID: 28258703 Review.
References
-
- Harari A., Graciotti M., Bassani-Sternberg M., Kandalaft L.E. Antitumour dendritic cell vaccination in a priming and boosting approach. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2020;19:635–652. - PubMed
-
- Chen L., Qin H., Zhao R., Zhao X., Lin L., Chen Y., Lin Y., Li Y., Qin Y., Li Y., et al. Bacterial cytoplasmic membranes synergistically enhance the antitumor activity of autologous cancer vaccines. Sci. Transl. Med. 2021;13 - PubMed
-
- Ma L., Diao L., Peng Z., Jia Y., Xie H., Li B., Ma J., Zhang M., Cheng L., Ding D., et al. Immunotherapy and Prevention of Cancer by Nanovaccines Loaded with Whole-Cell Components of Tumor Tissues or Cells. Adv. Mater. 2021;33 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

