Prognostic Value of Plasma Big Endothelin-1 in Patients Hospitalized for Heart Failure
- PMID: 40345830
- PMCID: PMC12314060
- DOI: 10.4070/kcj.2024.0354
Prognostic Value of Plasma Big Endothelin-1 in Patients Hospitalized for Heart Failure
Abstract
Background and objectives: Endothelin-1 (ET-1) is a potent vasoconstrictor and multifunctional neuroendocrine hormone that is closely associated with the pathophysiology of heart failure (HF). Currently, the evidence about the predictive value of big ET-1 in HF remains insufficient. This study aims to investigate the prognostic importance of big ET-1 in HF.
Methods: We examined the incidence of cardiovascular death in a single-center retrospective cohort of HF (de novo, worsening, or chronic included).
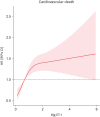
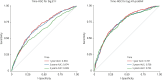
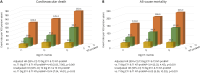
Results: The 4,368 hospitalized HF patients were enrolled. During the median follow-up of 875 (365-1,400) days, 851 (19.5%) patients had primary outcome events. Big ET-1 was independently associated with cardiovascular death as a continuous variable (hazard ratio [HR], 1.13; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.06-1.21; p<0.001) and by tertiles (HR, 1.35; 95% CI, 1.06-1.72; p=0.017 for tertile 2 and HR, 1.70; 95% CI, 1.32-2.19; p<0.001 for tertile 3). This pattern of risk was maintained after further adjustment for NT-proBNP (HR, 1.11; 95% CI, 1.03-1.19; p=0.006 for continuous variable, HR, 1.30; 95% CI, 1.02-1.67; p=0.035 for tertile 2, and HR, 1.69; 95% CI, 1.23-2.05; p=0.034 for tertile 3). Net reclassification index (NRI) and integrated discrimination improvement (IDI) analysis showed that big ET-1 provided additional predictive power in combination with NT-proBNP (NRI, 0.11; 95% CI, 0.04-0.17; p=0.012 and IDI, 0.012; 95% CI, 0.003-0.017; p<0.001).
Conclusions: Elevated big ET-1 was independently associated with cardiovascular death in patients with HF. Big ET-1 may be a promising indicator of HF prognosis. In combination with NT-proBNP, big ET-1 may provide incremental predictive information.
Keywords: Big endothelin-1; Biomarkers; Heart failure; Prognosis.
Copyright © 2025. The Korean Society of Cardiology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- GBD 2017 Disease and Injury Incidence and Prevalence Collaborators. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 354 diseases and injuries for 195 countries and territories, 1990-2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet. 2018;392:1789–1858. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Levin ER. Endothelins. N Engl J Med. 1995;333:356–363. - PubMed
-
- Barton M, Yanagisawa M. Endothelin: 30 years from discovery to therapy. Hypertension. 2019;74:1232–1265. - PubMed
-
- Cody RJ, Haas GJ, Binkley PF, Capers Q, Kelley R. Plasma endothelin correlates with the extent of pulmonary hypertension in patients with chronic congestive heart failure. Circulation. 1992;85:504–509. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

