Cerebral Amyloid Angiopathy-Related Inflammation in Iatrogenic Cerebral Amyloid Angiopathy
- PMID: 40345981
- PMCID: PMC12062866
- DOI: 10.1111/ene.70198
Cerebral Amyloid Angiopathy-Related Inflammation in Iatrogenic Cerebral Amyloid Angiopathy
Abstract
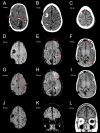
Introduction: Cerebral amyloid angiopathy (CAA) related inflammation (CAA-ri) is considered to be a distinct syndrome caused by an inflammatory response to amyloid-β deposition in the walls of small leptomeningeal and cortical vessels in patients with sporadic CAA. However, recent data suggest that inflammation might contribute to a broader range of CAA subtypes.
Results: We describe a case of probable iatrogenic CAA (iCAA), which manifested with multiple intracerebral haemorrhages complicated by the development of clinical and radiological features of CAA-ri, which responded to steroids. Clinical, neuroimaging and CSF data suggested possible co-existing Alzheimer's pathology.
Discussion: CAA-ri may occur in association with iCAA, suggesting that a broader spectrum of patients might benefit from steroid treatment than previously assumed.
Keywords: amyloid‐beta; cadaveric dura mater; cerebral amyloid angiopathy‐related inflammation; iatrogenic cerebral amyloid angiopathy; prion.
© 2025 The Author(s). European Journal of Neurology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of European Academy of Neurology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

