Enzymatic combinatorial synthesis of E-64 and related cysteine protease inhibitors
- PMID: 40346252
- PMCID: PMC12568646
- DOI: 10.1038/s41589-025-01907-2
Enzymatic combinatorial synthesis of E-64 and related cysteine protease inhibitors
Abstract
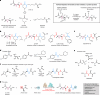
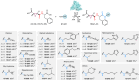
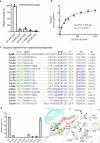
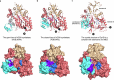
E-64 is an irreversible cysteine protease inhibitor prominently used in chemical biology and drug discovery. Here we uncover a nonribosomal peptide synthetase-independent biosynthetic pathway for E-64, which is widely conserved in fungi. The pathway starts with epoxidation of fumaric acid to the warhead (2S,3S)-trans-epoxysuccinic acid with an Fe(II)/α-ketoglutarate-dependent oxygenase, followed by successive condensation with an L-amino acid by an adenosine triphosphate grasp enzyme and with an amine by the fungal example of amide bond synthetase. Both amide bond-forming enzymes display notable biocatalytic potential, including scalability, stereoselectivity toward the warhead and broader substrate scopes in forming the amide bonds. Biocatalytic cascade with these amide bond-forming enzymes generated a library of cysteine protease inhibitors, leading to more potent cathepsin inhibitors. Additionally, one-pot reactions enabled the preparative synthesis of clinically relevant inhibitors. Our work highlights the importance of biosynthetic investigation for enzyme discovery and the potential of amide bond-forming enzymes in synthesizing small-molecule libraries.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures









References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

