Molecular regulation of whole genome DNA methylation in heat stress response of dairy cows
- PMID: 40346455
- PMCID: PMC12065190
- DOI: 10.1186/s12864-025-11683-x
Molecular regulation of whole genome DNA methylation in heat stress response of dairy cows
Abstract
Background: Heat stress seriously affects the production and health of dairy cows and is a key factor limiting the sustainable development of the dairy industry. DNA methylation serves as an important epigenetic regulatory mechanism closely associated with an animal's response to heat stress. However, the specific molecular mechanism of DNA methylation in cows' heat stress response is not fully understood.
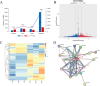
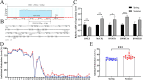
Results: In this study, whole genome bisulfite sequencing analysis of blood identified 49861 specific differentially methylated regions corresponding to 7613 differentially methylated genes between spring and summer dairy cows. Among them, 4069 the promoter region of differentially methylated genes were significantly enriched in key biological pathways such as substance transport, reactive oxygen species metabolism, signal transduction, and energy metabolism. By integrating the expression data of 4069 promoter differentially methylated genes, 157 genes were further screened, and their DNA methylation levels were negatively correlated with gene expression. The changes in DNLZ, GNAS, and SMAD5 genes were most significant, and network analysis showed that DNLZ gene has high connectivity in the protein-protein interaction network, indicating its potential key function in heat stress response. Experimental verification shows that under heat stress conditions, the methylation level of CpG islands in the promoter region of DNLZ gene significantly increases, and its methylation level is significantly negatively correlated with gene expression level. The Dual-luciferase reporter assays using constructs containing the DNLZ promoter reporter gene experiment further confirms that promoter methylation significantly inhibits DNLZ transcriptional activity, and the higher the degree of methylation, the stronger the inhibitory effect.
Conclusions: The research results provide new insights into the mechanism of heat stress-related DNA methylation in dairy cows, clarify the key roles of genes such as DNLZ, and provide potential target genes and epigenetic markers for the cultivation of heat-resistant dairy cows.
Keywords: DMG; DNA methylation; Dairy cows; Heat stress; WGBS.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: The animal experiment part of this study has been reviewed and approved by the Animal Experiment Ethics Committee, and the experimental procedures comply with the current animal welfare and research laws and regulations in China (approval number: SS-QX-2014–06). In addition, the animals used in the study have obtained the consent of Beijing Sanyuan Green Lotus Treasure Island Ranch. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Genome-wide methylation and transcriptome of blood neutrophils reveal the roles of DNA methylation in affecting transcription of protein-coding genes and miRNAs in E. coli-infected mastitis cows.BMC Genomics. 2020 Jan 30;21(1):102. doi: 10.1186/s12864-020-6526-z. BMC Genomics. 2020. PMID: 32000686 Free PMC article.
-
Whole-Genome Bisulfite Sequencing (WGBS) Analysis of Gossypium hirsutum under High-Temperature Stress Conditions.Genes (Basel). 2024 Sep 24;15(10):1241. doi: 10.3390/genes15101241. Genes (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39457365 Free PMC article.
-
Heat stress and immune response phenotype affect DNA methylation in blood mononuclear cells from Holstein dairy cows.Sci Rep. 2021 May 31;11(1):11371. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-89951-5. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34059695 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative genome-wide DNA methylation analysis reveals epigenomic differences in response to heat-humidity stress in Bombyx mori.Int J Biol Macromol. 2020 Dec 1;164:3771-3779. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.08.251. Epub 2020 Sep 3. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020. PMID: 32891645
-
Preweaning heat stress alters liver transcriptome and DNA methylation in dairy calves.J Dairy Sci. 2025 Apr;108(4):4390-4402. doi: 10.3168/jds.2024-25975. Epub 2025 Jan 30. J Dairy Sci. 2025. PMID: 39892602
Cited by
-
piRNAs as Potential Regulators of Mammary Gland Development and Pathology in Livestock.Vet Sci. 2025 Jun 17;12(6):594. doi: 10.3390/vetsci12060594. Vet Sci. 2025. PMID: 40559831 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mini review: Studying epigenomic alterations can shed light on coping and adaptive abilities during heat stress in monogastric livestock.Front Genet. 2025 Aug 1;16:1561804. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2025.1561804. eCollection 2025. Front Genet. 2025. PMID: 40822283 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

