Study on the correlation between oxidized low- density lipoprotein and oxidized high- density lipoprotein with type 2 diabetes complicated by pulmonary tuberculosis
- PMID: 40346508
- PMCID: PMC12065307
- DOI: 10.1186/s12890-025-03669-y
Study on the correlation between oxidized low- density lipoprotein and oxidized high- density lipoprotein with type 2 diabetes complicated by pulmonary tuberculosis
Abstract
Objectives: This study aims to investigate the correlations between oxidized lipoproteins, specifically oxidized low-density lipoprotein (oxLDL) and oxidized high-density lipoprotein (oxHDL), and the comorbidities of T2DM and PTB (T2DM + PTB).
Methods: This prospective study included 360 cases from May 2022 to May 2023. The cohort consisted of 60 cases of pure hyperlipidemia, 100 cases of PTB, 100 cases of T2DM, and 100 cases of T2DM + PTB. Each of the PTB, T2DM, and T2DM + PTB groups was further subdivided into a normal lipid subgroup (40 cases) and a hyperlipidemia subgroup (60 cases). Additionally, 40 healthy individuals served as a control group. The age range of participants spanned from 40.8 ± 7.36 to 56.34 ± 11.52 years. Venous blood samples were collected from each group to measure levels of HbA1c, insulin (INS), fasting serum glucose (FSG), total cholesterol (TC), triglycerides (TG), HDL-C, LDL-C, apolipoprotein A-I(ApoA I), apolipoprotein B(Apo B), oxidized low-density lipoprotein (oxLDL), and oxidized high-density lipoprotein (oxHDL). Multivariate logistic regression analysis assessed the association of oxLDL and oxHDL levels with PTB.
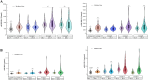
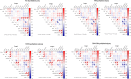
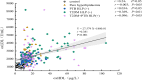
Results: The levels of oxLDL and oxHDL in the pure hyperlipidemia group, PTB hyperlipidemia subgroup,T2DM hyperlipidemia subgroup, and T2DM + PTB hyperlipidemia subgroup were significantly elevated compared to those in the control group. Correlation analysis demonstrated a positive correlation between TG and LDL-C with oxLDL in the T2DM hyperlipidemia subgroup and the T2DM + PTB hyperlipidemia subgroup. TC and LDL-C were also positively correlated with oxLDL in the PTB hyperlipidemia subgroup. All hyperlipidemia groups exhibited a positive correlation between TG and oxHDL. Multivariate logistic regression analysis showed that oxLDL ≥2362U/L~<4724 U/L (more than 2 times higher than the control group) and oxHDL ≥ 26 μg/L (more than 4 times higher than the control group) were relative risk factors for PTB.
Conclusion: Significantly elevated oxLDL and oxHDL levels may be risk factors for PTB and may influence the comorbidity of T2DM and PTB. Further evaluation of pathological levels with oxLDL levels exceeding twice the control group and oxHDL levels exceeding four times the control group is recommended.
Keywords: Blood lipid; Oxidized high-density lipoprotein; Oxidized low-density lipoprotein; Pulmonary tuberculosis; Type 2 diabetes mellitus.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Each participant inT2DM and PTB which was conducted under the Ethics Committee of Shenzhen Chronic Disease Prevention Center before taking part (SZCCC- 2022–010 - 01 -YJ). All participants have given informed consent for this study. The Ethics Committee of Shenzhen Chronic Disease Prevention Center approved this study. In addition, the Declaration of Helsinki was followed during our research. The necessary standards and legislation were followed in the execution of all procedures, including the declarations in. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Oxidized HDL and LDL in adolescents with type 2 diabetes compared to normal weight and obese peers.J Diabetes Complications. 2015 Jul;29(5):679-85. doi: 10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2015.03.015. Epub 2015 Apr 6. J Diabetes Complications. 2015. PMID: 25881918 Free PMC article.
-
Associations of Circulating Oxidized LDL and Conventional Biomarkers of Cardiovascular Disease in a Cross-Sectional Study of the Navajo Population.PLoS One. 2016 Mar 3;11(3):e0143102. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0143102. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 26938991 Free PMC article.
-
Elevated Levels of Serum β2-Glycoprotein I/Oxidized Low-Density Lipoprotein Complexes Are Associated with Cerebral Infarction in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.Med Sci Monit. 2018 Feb 28;24:1232-1240. doi: 10.12659/msm.907078. Med Sci Monit. 2018. PMID: 29489742 Free PMC article.
-
The Oxidized Lipoproteins In Vivo: Its Diversity and Behavior in the Human Circulation.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Mar 17;24(6):5747. doi: 10.3390/ijms24065747. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36982815 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structure and Dynamics of Oxidized Lipoproteins In Vivo: Roles of High-Density Lipoprotein.Biomedicines. 2021 Jun 8;9(6):655. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9060655. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 34201176 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sinclair A, Saeedi P, Kaundal A, Karuranga S, Williams R. Diabetes and global aging among 65–99 year-old adults: Findings from theInternational Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas, 9th edition[J]. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2020;162: 108078. 10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108078. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization. Global Tuberculosis Report 2022. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2022.
-
- Ping PA, Zakaria R, Islam MA, Yaacob LH, Muhamad R, Zahiruddin-Wan -Mohamad WM, Yusoff HM. Prevalence and risk factors of latent tuberculosis infection (LTBI) in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) [J]. Int J Environ Res Public Health, 2021, 18(1):305. 10.3390/ijerph1801-0305. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- No.82373641/the National Natural Science Foundation of China
- No.82373641/the National Natural Science Foundation of China
- No.82373641/the National Natural Science Foundation of China
- No.82373641/the National Natural Science Foundation of China
- No.82373641/the National Natural Science Foundation of China
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

