Tertiary lymphoid structures in gliomas: impact on tumour immunity and progression
- PMID: 40346572
- PMCID: PMC12065291
- DOI: 10.1186/s12967-025-06510-6
Tertiary lymphoid structures in gliomas: impact on tumour immunity and progression
Abstract
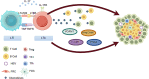
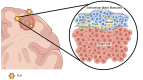
Tertiary lymphoid structures (TLSs) are ectopic lymphoid formations that develop in chronically inflamed tissues, including various solid tumours. In the context of gliomas, the presence of TLSs has recently attracted considerable attention because of their potential implications in tumour immunology and therapy. The tumour immune microenvironment (TIME) plays a crucial role in cancer progression, and tumour-infiltrating immune cells (TILs) are key players in this environment. These immune cell aggregates, known as TLSs, display distinct characteristics across different solid tumours. However, central nervous system (CNS) tumours are highly heterogeneous, and the immune environment within these tumours is often more deficient than that of peripheral tissue tumours. This leads to differences in the formation and function of TLSs in CNS tumours. These variations are particularly relevant in the context of glioma immunotherapy and could have important implications for treatment strategies. This review focuses on the composition and function of TLSs, examines the complexity of the glioblastoma (GBM) immune microenvironment, and highlights the unique characteristics of TLSs in GBM, providing new theoretical insights and practical foundations for targeting TLSs in glioma immunotherapy.
Keywords: Gliomas; Immunotherapy; Tertiary lymphoid structure.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: All the authors have read and approved the final manuscript. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Tertiary lymphoid structures in the era of cancer immunotherapy.Nat Rev Cancer. 2019 Jun;19(6):307-325. doi: 10.1038/s41568-019-0144-6. Nat Rev Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31092904 Review.
-
Comparative impact of tertiary lymphoid structures and tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in cholangiocarcinoma.J Immunother Cancer. 2025 Jan 27;13(1):e010173. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2024-010173. J Immunother Cancer. 2025. PMID: 39870490 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Tertiary lymphoid structures and cancer immunotherapy: From bench to bedside.Med. 2025 Jan 10;6(1):100546. doi: 10.1016/j.medj.2024.10.023. Med. 2025. PMID: 39798544 Review.
-
Tertiary lymphoid structures and their therapeutic implications in cancer.Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2024 Oct;47(5):1579-1592. doi: 10.1007/s13402-024-00975-1. Epub 2024 Aug 12. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 2024. PMID: 39133439 Review.
-
Integrated analysis of tertiary lymphoid structures and immune infiltration in ccRCC microenvironment revealed their clinical significances: a multicenter cohort study.J Immunother Cancer. 2024 Jun 21;12(6):e008613. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2023-008613. J Immunother Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38908856 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hou X, Li X, Han Y, Xu H, Xie Y, Zhou T, Xue T, Qian X, Li J, Wang HC, et al. Triple-negative breast cancer survival prediction using artificial intelligence through integrated analysis of tertiary lymphoid structures and tumor budding. Cancer. 2024;130:1499–512. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- No. 82103429/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- No. 82403377/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- No. 2023ZD0510300/Noncommunicable Chronic Diseases-National Science and Technology Major Project
- No. Y-Young2024-0138/Beijing Xisike Clinical Oncology Research Foundation
- No. 2024M750538/China Postdoctoral Science Foundation
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical