Numerical simulation of stability of diffusion depth of deterrents into cylindrical nitrocellulose composite under different conditions
- PMID: 40346579
- PMCID: PMC12065235
- DOI: 10.1186/s13065-025-01495-1
Numerical simulation of stability of diffusion depth of deterrents into cylindrical nitrocellulose composite under different conditions
Abstract
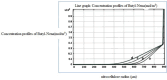
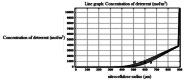
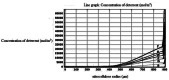
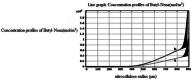
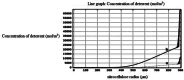
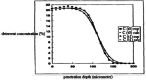
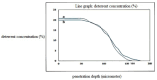
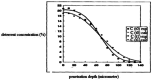
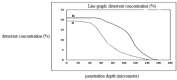
In this study, evaluation and prediction of diffusion depth of deterrents of Butyl-NENA and Polyethylene-glycol-di-methacrylate into the propellant and the effect of different conditions on diffusion stability, such as variations of concentration, temperature and aging with time, were performed by using COMSOL Multi-physics 4.4 to lower the laboratory costs and saving time. Diagrams indicated that diffusion of deterrents occurs to a certain depth of the propellant radius and variations of concentration in allowed ranges, does not affect the final diffusion depth significantly. Also, variations in temperature and aging with time had a little effect on the diffusion depth. Results showed that substances were used for nitrocellulose propellant coating, have excellent diffusion stability. simulation results were compared torelated experimental results and showed good agreement with them. concentration profiles of Butyl-Nena at two concentrations of 10% and 20%, measured at 70˚C for 10 h. the concentration profile at 10% is shown, and a gentle increase in concentration is observed for small to medium radii. While the 20% profile shows a faster and more significant increase in concentration, reaching high values at larger radii. These results indicate a significant effect of Butyl-Nena concentration on its concentration distribution pattern with increasing radius. the concentration profiles of deterrent polymers at two concentrations of 2% and 12%, measured at 70˚C for 10 h. the deterrent concentration at 2% gradually increases and reaches significant values, while at 12%, the concentration rapidly approaches a maximum value. These results indicate a significant effect of deterrent concentration on the concentration profiles with increasing radius.The aim of the present work was predicting the influence of various conditions such as, concentration, temperature and time on deterrents diffusion stability by COMSOL Multi-physics.
Keywords: COMSOL Multi-physics; Deterrent; Diffusion; Nitrocellulose; Simulation; Stability.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Racoveanu A, Skyler DA, Leipzig BK, Dawley SK. Novel Plasticizer For Im Compliant Solid Propellants, National Defense Industrial Association Insensitive Munitions & Energetic Materials Technology Symposium, Tucson, Arizona, 2009.
-
- Jelisavac L, Bajramovic D. Identification And Quantitative Determination Of Poly-Ethylene-Glycol-Dimethacrylate Deterrent In Single-Base Gun Propellants. Scientific-Technical Review. 2005;Lv(2).
-
- The Institution Of Chemical Research And Industries Of Iran handbook. 2002. 5.133- 5.149.
-
- Edwards JS, Ren TX, Jozefowicz R. Using Computational Fluid Dynamics (Cfd) To Solve Mine Safety And Health Problems, Technical Proceedings. Application Of Computers And Operations Research In The Minerals Industries. 1995. 41–47. Australia.
-
- Harvard L, Thomas HP, David WZ. Fundamentals of computational fluid dynamics. Nasa Ames Research Center; 1999:267.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
