Comparative efficacy and acceptability of novel biologics in the treatment of myasthenia gravis: systematic review and network meta-analysis of randomized trials
- PMID: 40346603
- PMCID: PMC12063394
- DOI: 10.1186/s13643-025-02859-3
Comparative efficacy and acceptability of novel biologics in the treatment of myasthenia gravis: systematic review and network meta-analysis of randomized trials
Abstract
Background: Myasthenia gravis (MG) is a chronic autoimmune disorder affecting the neuromuscular junction. The emergence of molecular therapies, such as monoclonal antibodies, B-cell-depleting agents, and chimeric antigen receptor T-cell-based therapies, has the potential to transform the treatment landscape for myasthenia gravis. The clinical efficacy of novel biologics in the treatment of individuals with myasthenia gravis is still a subject of debate. The objective was to compare and rank the efficacy and acceptability of novel biologics in the treatment of individuals with MG through a network meta-analysis.
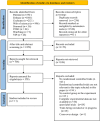
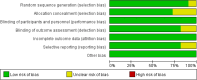
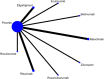
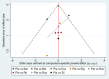
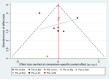
Methods: This systematic review and network meta-analysis (NMA) involved a comprehensive search for published randomized controlled trials (RCTs) across several databases, including PubMed, Web of Science, Embase, Cochrane Library, SinoMed, CNKI, Wanfang, and VIP, covering articles published from inception until July 3, 2024. We included randomized controlled trials involving patients with myasthenia gravis. The main outcome was the overall symptomatology. Random-effects pairwise meta-analyses and network meta-analyses (NMAs) were conducted to compute standardized mean differences (SMDs) or risk ratios with 95% confidence intervals (CIs). The research process did not include individuals with lived experience. The studies' quality was evaluated utilizing the risk-of-bias assessment tool created by the Cochrane Collaboration. Network meta-analysis was performed utilizing Stata 16 and R4.2.3.
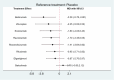
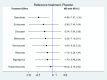
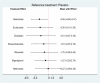
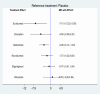
Results: Eleven RCTs including 840 participants with myasthenia gravis were eligible. Belimumab improvement of the MG-ADL score is compared to placebo (MD = - 3.29, 95% CI (- 5.78, - 0.80), P < 0.05). Compared to placebo, batoclimab enhanced the QMG score (MD = - 4.46, 95% CI (- 7.57, - 1.35), P < 0.05) and the MGC score (MD = - 3.58, 95% CI (- 6.68, - 0.47), P < 0.05). Eculizumab improvement of the MG-QoL 15r score is compared to placebo (MD = - 7.10, 95% CI (- 12.20, - 2.00), P < 0.05). Regarding adverse reactions, we found no difference in the network comparison of novel biologics compared to placebo, but this conclusion requires further validation through rigorous research.
Conclusions: This study provides an updated, relative rank-order efficacy of novel biologics therapies for myasthenia gravis. These data may help inform the design and sample size calculation of future clinical trials and assist selection of combination therapy.
Systematic review registration: PROSPERO CRD42024559757.
Keywords: Efficacy and acceptability; Myasthenia gravis; Network meta-analysis; Novel biologics.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1(1):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. PMID: 31917873 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Dec 22;12(12):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. PMID: 29271481 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Drugs for preventing postoperative nausea and vomiting in adults after general anaesthesia: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Oct 19;10(10):CD012859. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012859.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 33075160 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of biological interventions for ulcerative colitis on health-related quality of life.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Sep 22;2015(9):CD008655. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008655.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. PMID: 26393522 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Li J, Chen Y, Cao W, et al. Efgartigimod alpha, a neonatal Fc receptor antagonist for the treatment of generalised myasthenia gravis. J Clin Pharmacother. 2024;22(04):21–5.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- No. 2022YFC3501301;2022YFC3501305/the National Key Research and Development Program of China
- No. 82205107/the National Natural Science Foundation of China
- No. 20210101212JC/the Science and Technology Development Plan Project of Jilin Province, China
- 202310/the Youth discipline backbone training project of Changchun university of Chinese Medicine
- 2022-QNRC2-A08/the Yong Elite Scientists Sponsorship Program by CACM
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

