Advancing ORFV-Based Therapeutics to the Clinical Stage
- PMID: 40346732
- PMCID: PMC12064845
- DOI: 10.1002/rmv.70038
Advancing ORFV-Based Therapeutics to the Clinical Stage
Abstract
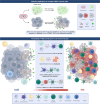
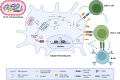
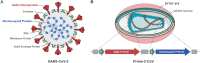
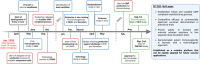
The Orf virus (ORFV) is the prototype member of the parapoxvirus family and has long been recognized for its robust immunogenicity, favourable safety profile and its ability to stimulate both cellular and humoural immune responses without inducing significant anti-vector immunity. Despite these inherent advantages, early applications of ORFV-based technologies were limited by challenges in manufacturing scalability and uncertainties regarding clinical safety in humans. However, recent breakthroughs have transformed this therapeutic landscape. A landmark achievement is the development of Prime-2-CoV, an ORFV-based anti-COVID-19 vaccine that has advanced into human clinical trials, providing the first clinical evidence of live ORFV's feasibility, safety and immunogenicity. This milestone, together with the establishment of a good manufacturing practice (GMP)-compliant production process and comprehensive preclinical evaluations, has laid a robust foundation for broader clinical applications of ORFV-based therapeutics. Moreover, the use of ORFV as an oncolytic virus therapy has shown promising results, effectively converting immunologically 'cold' tumours into 'hot' ones, underscoring its versatility as a therapeutic platform. In this review, we critically assess recent advances in ORFV-based therapeutics, with a particular focus on vaccine development and oncolytic virotherapy (OVT). We thoroughly discuss the milestones and impact of the first ORFV-based clinical trial, outline strategies for optimizing the technology and provide insights into overcoming remaining challenges. Collectively, these advancements position ORFV as a highly promising and versatile platform for next-generation prophylactic and therapeutic interventions in both human and veterinary medicine, while also providing a roadmap for future innovations.
Keywords: ORFV; immune stimulation; immunogenic cell death; oncolytic virus; orf virus; parapoxvirus; vaccine; viral vector.
© 2025 The Author(s). Reviews in Medical Virology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
R.A. holds ownership interest in Prime Vector Technologies GmbH, a company involved in the development of ORFV‐based vaccines. Additionally, R.A. is an inventor of patents related to ORFV, including a patent application of Prime‐2‐CoV_Beta (EP23730776). M.H. declares no competing interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

