SGLT2 Inhibition by Enavogliflozin Significantly Reduces Aβ Pathology and Restores Cognitive Function via Upregulation of Microglial AMPK Signaling in 5XFAD Mouse Model of Alzheimer's Disease
- PMID: 40346951
- PMCID: PMC12341776
- DOI: 10.1111/acel.70101
SGLT2 Inhibition by Enavogliflozin Significantly Reduces Aβ Pathology and Restores Cognitive Function via Upregulation of Microglial AMPK Signaling in 5XFAD Mouse Model of Alzheimer's Disease
Abstract
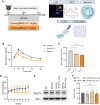
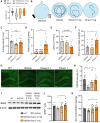
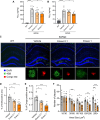
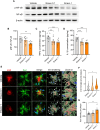
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder characterized by cognitive decline. Metabolic dysfunctions, particularly type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), have been implicated in AD pathogenesis, highlighting the potential for novel therapeutic approaches targeting shared underlying mechanisms. Here, we investigate sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibition as a therapeutic strategy for AD using Enavogliflozin, a potent SGLT2 inhibitor, in the 5XFAD mouse model. Five-month-old 5XFAD mice were treated with Enavogliflozin (0.1 or 1 mg/kg) or vehicle for 8 weeks. The higher dose significantly improved cognitive performance in Y-maze and Morris Water Maze tests, which correlated with enhanced synaptic plasticity and increased acetylcholine levels. Moreover, Enavogliflozin treatment reduced Aβ pathology and plaque burden, particularly affecting larger plaques. Mechanistically, SGLT2 inhibition attenuated neuroinflammation by suppressing NF-κB signaling and proinflammatory cytokine production while promoting microglial recruitment to plaques. In vitro and ex vivo analyses further revealed that Enavogliflozin enhances microglial phagocytic capacity via AMPK-mediated mitochondrial biogenesis and function. These findings highlight the multifaceted neuroprotective effects of SGLT2 inhibition in AD, demonstrating its potential to mitigate pathology and improve cognitive function. By uncovering its impact on neuroinflammation and microglial function, this study establishes SGLT2 inhibition as a promising therapeutic avenue for AD and other neurodegenerative disorders.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; SGLT2 inhibition; amyloid‐beta; anti‐diabetic drugs; cognitive function; neuroinflammation.
© 2025 The Author(s). Aging Cell published by Anatomical Society and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Atri, A. , Feldman H. H., Hansen C. T., et al. 2022. “Evoke and Evoke+: Design of Two Large‐Scale, Double‐Blind, Placebo‐Controlled, Phase 3 Studies Evaluating the Neuroprotective Effects of Semaglutide in Early Alzheimer's Disease.” Alzheimer's & Dementia 18, no. S10: e062415. 10.1002/alz.062415. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

