Comprehensive αβ T-Cell Receptor Repertoire Analysis Reveals a Unique CD8+ TCR Landscape in DOCK8-Deficient Patients
- PMID: 40346988
- PMCID: PMC12444818
- DOI: 10.1111/all.16580
Comprehensive αβ T-Cell Receptor Repertoire Analysis Reveals a Unique CD8+ TCR Landscape in DOCK8-Deficient Patients
Abstract
Background: Dedicator of cytokinesis protein 8 (DOCK8) is a guanine nucleotide exchange factor highly expressed in, and critical for, the function of various innate and adaptive immune cells. DOCK8 deficiency leads to combined immunodeficiency characterized by susceptibility to infections, autoimmunity, and a severe Th2-type immune response. While dysfunction in various T cell subsets has been implicated in these phenotypes, a comprehensive analysis of the T-cell receptor (TCR) repertoire in these patients has not yet been documented. This study investigates the αβ TCR repertoire in DOCK8-deficient patients to identify features related to disease pathogenesis and explore the potential role of TCR repertoire alterations in disease development.
Methods: We compared immune repertoire profiles determined by high-throughput TCR sequencing of circulating CD4+ and CD8+ T cells from patients with DOCK8 deficiency (n = 10) to healthy controls (n = 7) and patients with ataxia-telangiectasia (AT) (n = 5).
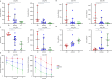
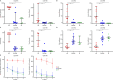
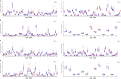
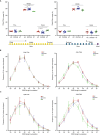
Results: Different diversity analyses revealed a restricted TRA and TRB repertoire in both CD4+ and CD8+ T cells from DOCK8-deficient patients, with the restriction being more pronounced in CD8+ T cells. Skewed usage of individual variable (V) and joining (J) genes and potentially self-reactive CD8+ T cell clones, as determined by hydrophobicity and cysteine indices, were identified in DOCK8-deficient patients.
Conclusion: Our study represents the most comprehensive immune repertoire analysis in DOCK8 deficiency. The identification of a significantly restricted αβ TCR repertoire, along with the detection of potentially autoreactive clones, highlights the crucial role of immune repertoire profiling in elucidating the pathogenesis of DOCK8 deficiency.
Keywords: DOCK8 deficiency; T‐cell receptor repertoire; autoimmunity; immune repertoire sequencing.
© 2025 The Author(s). Allergy published by European Academy of Allergy and Clinical Immunology and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Engelhardt K. R., McGhee S., Winkler S., et al., “Large Deletions and Point Mutations Involving the Dedicator of Cytokinesis 8 (DOCK8) in the Autosomal‐Recessive Form of Hyper‐IgE Syndrome,” Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 124, no. 6 (2009): 1289–1302, 10.1016/j.jaci.2009.10.038. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- The Hospital Research Foundation
- Türkiye Bilimsel ve Teknolojik Araştırma Kurumu
- Hacettepe Üniversitesi
- 121S667/The Scientific and Technological Research Council of Türkiye (TUBITAK)
- 123S777/The Scientific and Technological Research Council of Türkiye (TUBITAK)
- THD-2022-20180/The Scientific Research Projects Coordination Unit of Hacettepe University
- TKB-2021-19539/The Scientific Research Projects Coordination Unit of Hacettepe University
- THD-2024-21191/The Scientific Research Projects Coordination Unit of Hacettepe University
- ADT-2025-11514/The Marmara University Scientific Research Project Coordination Unit
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

