The human photosensitive epilepsy model for clinical proof-of-principle trials of novel antiseizure medications: 2. Analysis of drug trials and predictive value of the model
- PMID: 40347110
- PMCID: PMC12371661
- DOI: 10.1111/epi.18444
The human photosensitive epilepsy model for clinical proof-of-principle trials of novel antiseizure medications: 2. Analysis of drug trials and predictive value of the model
Abstract
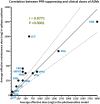
Clinical development of novel antiseizure medications (ASMs) would benefit from an early proof of principle (POP) model. The photosensitivity model, which uses the photoparoxysmal electroencephalographic response (PPR) as a surrogate of seizures, is currently the only human model that allows POP trials of investigational compounds after a single drug administration. Typically, trials in this model are performed as single-blinded, placebo-controlled phase IIa POP studies, evaluating a range of doses in small groups of epilepsy patients. In the second part of this review, based on the background information provided in Part 1, we analyze the outcome of all published trials performed over roughly 50 years. Many of the 35 drugs tested in the model were also examined in traditional add-on trials in patients with epilepsy, thus allowing analysis of the predictivity of the model. Drugs were categorized into three groups: drugs that suppressed PPR; drugs that exerted no effect on PPR; and drugs that increased PPR, indicating a proconvulsant effect. For the vast majority of drugs, the model correctly predicted the drugs' activity during long-term studies in patients with different types of epilepsy, including focal onset epilepsies. For some investigational compounds, the model detected proconvulsant activity that had not been observed in preclinical animal experiments and phase I studies in healthy volunteers, demonstrating the value of the model for adverse event assessment in patients with epilepsy. Limitations of the model are that it does not predict the extent of drug resistance of patients' seizures during chronic administration or efficacy differentiation of the novel drug from existing ASMs. Photosensitive POP trials are a useful tool to quantitatively predict drug efficacy and in aiding dose selection for subsequent larger phase IIb trials with chronic drug administration.
Keywords: animal models; intermittent photic stimulation; mechanism of action; pharmacodynamics; pharmacokinetics; photoparoxysmal EEG response; proof of concept.
© 2025 The Author(s). Epilepsia published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of International League Against Epilepsy.
Conflict of interest statement
D.K.‐N.T. has in the past 5 years received consultancy fees from UCB, Otsuka, SK, Idorsia, Lundbeck, Jazz, and Praxis. She also receives royalties from Wolters Kluwer (UpToDate). W.L. is cofounder and CSO of PrevEp (Bethesda, MD, USA). He has in the past 5 years received consultancy fees from Lundbeck, Angelini, Clexio, Selene, Axonis, SynapCell, Sintetica, ND Capital, Atlas Venture, Cogent Biosolutions, Ovid, Idorsia, and Addex. We confirm that we have read the Journal's position on issues involved in ethical publication and affirm that this report is consistent with those guidelines.
Figures

References
-
- Fisher RS, Acharya JN, Baumer FM, French JA, Parisi P, Solodar JH, et al. Visually sensitive seizures: an updated review by the Epilepsy Foundation. Epilepsia. 2022;63:739–768. - PubMed
-
- Yuen ES, Sims JR. How predictive are photosensitive epilepsy models as proof of principle trials for epilepsy? Seizure. 2014;23:490–493. - PubMed
-
- Binnie CD, Kasteleijn‐Nolst Trenite DG, De Korte R. Photosensitivity as a model for acute antiepileptic drug studies. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1986;63:35–41. - PubMed
-
- Rimmer EM, Milligan NM, Richens A. A comparison of the acute effect of single doses of vigabatrin and sodium valproate on photosensitivity in epileptic patients. Epilepsy Res. 1987;1:339–346. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

