Asia-Pacific Menopause Federation Consensus Statement on the Management of Menopause 2024
- PMID: 40347161
- PMCID: PMC12070119
- DOI: 10.6118/jmm.25104
Asia-Pacific Menopause Federation Consensus Statement on the Management of Menopause 2024
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Asia-Pacific Menopause Federation Consensus Statement on the Management of Menopause 2024.J Menopausal Med. 2025 Aug;31(2):130-131. doi: 10.6118/jmm.25104r. J Menopausal Med. 2025. PMID: 40954997 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Objectives: This study aimed to achieve expert consensus on menopause management in the Asia-Pacific region, taking into account patient diversity, the latest evidence, and current treatment options.
Methods: A focused literature search was performed to identify clinical practice statements on menopause management. Menopause experts were nominated by members of the Asia-Pacific Menopause Federation (APMF) society. A modified Delphi methodology, involving iterative rounds of anonymous surveys, was employed until consensus was reached for each statement. Consensus was defined as ≥ 70% of experts voting 'agree' or 'strongly agree' for a given clinical practice statement.
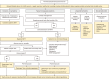
Results: A total of 39 participants from 14 different APMF member societies were involved. Eighty-five clinical practice statements reached a consensus. Based on the clinical practice statements, an algorithm was created as a tool to guide clinicians on menopause management. APMF experts agreed that, in addition to vasomotor symptoms, Asian women experiencing somatic or psychological symptoms may also benefit from treatment with menopausal hormone therapy (MHT). MHT should also be considered for the prevention of osteoporosis in asymptomatic peri- and postmenopausal women.
Conclusions: This APMF consensus statement supersedes the previous one published in 2008. It provides guidance to gynecologists, endocrinologists, family physicians, and other healthcare professionals in delivering optimal care to menopausal women in the ethnically and culturally diverse Asia-Pacific region.
Keywords: Asia-Pacific; Menopausal hormone therapy; Menopause; Osteoporosis; Perimenopause.
Copyright © by The Korean Society of Menopause.
Conflict of interest statement
Sonia Davison has received honoraria for educational presentations in the area of women's health and menopause from the following entities: Astellas Pharma Australia Pty Ltd., Pfizer Inc., Theramex HQ UK Ltd., Besins Healthcare, Lawley Pharmaceuticals, Jean Hailes for Womens Health, Australasian Menopause Society, HealthEd.
Figures

References
-
- United Nations (UN) World population prospects 2024: summary of results. UN; 2024. [cited 2025 Mar 30]. Available from: https://desapublications.un.org/publications/world-populationprospects-2....
-
- Kirchengast S. Menopause in a globalized world - a systematic literature review focussing on the challenge of health problems associated with menopausal transition among women with a migration background. Maturitas. 2024;187:108045. - PubMed
-
- Ang SB, How CH. Menopause: an important milestone in women's health. Singapore Med J. 2013;54:60–63. - PubMed
-
- Islam MR, Gartoulla P, Bell RJ, Fradkin P, Davis SR. Prevalence of menopausal symptoms in Asian midlife women: a systematic review. Climacteric. 2015;18:157–176. - PubMed
-
- Shorey S, Ng ED. The experiences and needs of Asian women experiencing menopausal symptoms: a meta-synthesis. Menopause. 2019;26:557–569. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

