Push Forward Clinical Management of Hematological Toxicity due to Lenalidomide Overexposure: Model-Informed Precision Dosing for Chinese Population With Renal Insufficiency
- PMID: 40347488
- PMCID: PMC12256667
- DOI: 10.1002/psp4.70040
Push Forward Clinical Management of Hematological Toxicity due to Lenalidomide Overexposure: Model-Informed Precision Dosing for Chinese Population With Renal Insufficiency
Abstract
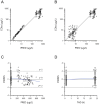
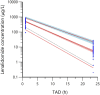
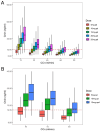
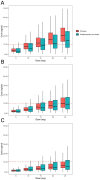
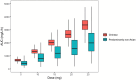
Dose-dependent hematological toxicity of lenalidomide has been reported previously, and thus, there is a clinical need for dose individualization to manage toxicities. The objectives of this study were to explore optimal individualized dosing regimens for Chinese B-cell malignancies patients with varying degrees of renal function, and to push forward clinical management of hematological toxicity due to lenalidomide overexposure. A total of 164 plasma concentrations of lenalidomide were obtained from 97 Chinese patients with multiple myeloma (MM) and B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) from a multicenter prospective study. A population pharmacokinetic (PopPK) model for lenalidomide was developed by nonlinear mixed effect modeling. A Monte Carlo simulation was conducted to recommend model-informed precision dosing (MIPD) for patients with varying degrees of renal function. A one-compartment model with first-order elimination best described the pharmacokinetics of lenalidomide. The population typical values of lenalidomide were as follows: absorption rate constant (Ka) of 8.34 h-1, apparent volume of distribution (V/F) of 37.4 L, and apparent clearance (CL/F) of 7.4 L/h. Creatinine clearance (CCr) was identified as a major covariate for CL/F, whereas other demographics or clinical characteristics had no significant effect on the model. When given the identical dose, Chinese patients exhibited a higher exposure than the predominantly non-Asian population at all dosage regimens, especially in patients with severe renal damage (CCr < 30 mL/min). For Chinese patients with CCr of 15-30 mL/min who do not require dialysis usually, compared to the dosing regimen of 15 mg every other day recommended by drug instructions, there exists a relatively lower risk of hematotoxicity when administered with 5 or 10 mg/day. For Chinese patients with CCr < 15 mL/min requiring dialysis, there was still a certain level of hematotoxicity risk associated with the dosing regimen of 5 mg/day recommended by drug instructions. The PopPK Model-based simulation suggests that Chinese patients may exhibit a higher exposure than the predominantly non-Asian population. For patients with severely impaired renal function, compared to dose adjustment in accordance with drug instructions, an individualized dosage strategy based on therapeutic drug monitoring (TDM) and MIPD would be preferable from a safety perspective.
Keywords: B‐cell malignancies; lenalidomide; model‐informed precision dosing; population pharmacokinetics; therapeutic drug monitoring.
© 2025 The Author(s). CPT: Pharmacometrics & Systems Pharmacology published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of American Society for Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Gonzalez‐Lugo J. D., Kambhampati S., Yacoub A., et al., “Lenalidomide and Eltrombopag for Treatment of Low‐Or Intermediate‐Risk Myelodysplastic Syndrome: Result of a Phase II Clinical Trial,” Clinical Cancer Research 29 (2023): 60–66. - PubMed
-
- Blair H. A., “Lenalidomide: A Review in Previously Treated Follicular Lymphoma,” Drugs 80 (2020): 1337–1344. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

