Acid sphingomyelinase recruits palmitoylated CD36 to membrane rafts and enhances lipid uptake
- PMID: 40348192
- PMCID: PMC12180984
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jbc.2025.110213
Acid sphingomyelinase recruits palmitoylated CD36 to membrane rafts and enhances lipid uptake
Abstract
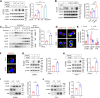
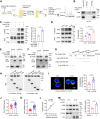
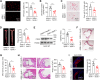
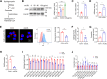
CD36 palmitoylation increases its membrane localization and is required for CD36-mediated uptake of oxidized low-density lipoprotein (oxLDL). Acid sphingomyelinase (ASMase) is transported to the plasma membrane, where it promotes lipid raft clustering, facilitating membrane protein anchoring for biological functions. We investigated the effects of oxLDL on CD36 palmitoylation and explored the role of ASMase in CD36 membrane translocation. We found that oxLDL increased CD36 palmitoylation and drives its intracellular trafficking from the endoplasmic reticulum to the plasma membrane lipid rafts in macrophages. Affinity purification followed by mass spectrometry analysis identified CD36 bound to ASMase in the plasma membrane. The CD36/ASMase binding was enhanced by oxLDL treatment. Genetic ablation and pharmacological inhibition of ASMase reduced CD36 recruitment to lipid rafts and inhibited CD36 intracellular signaling and lipid uptake. Moreover, inhibiting Sortilin to block ASMase intracellular trafficking and reduce membrane ASMase also caused a sharp decrease in the amount of membrane CD36. In addition, ASMase overexpression dramatically promoted palmitoylated CD36 membrane localization but not CD36 without palmitoylation, in which the modification was inhibited by 2-bromopalmitate (2-BP) treatment or point mutation at the palmitoylation site. Moreover, ASMase knockout inhibited CD36 membrane recruitment both in peritoneal macrophages and in the aorta, and attenuated lipid accumulation in atherosclerotic plaques in mice. Finally, we found oxLDL activated extracellular signal-regulated kinase1/2 (ERK1/2)/specificity protein (SP1) signaling, upregulating ASMase transcription and promoting sphingomyelin catabolism. Therefore, these data demonstrate that ASMase expression induced by oxLDL is required for palmitoylated CD36 membrane translocation during foam cell formation in macrophages.
Keywords: CD36; acid sphingomyelinase; foam cell; lipid raft; palmitoylation.
Copyright © 2025 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Acid sphingomyelinase promotes diabetic cardiomyopathy via disruption of mitochondrial calcium homeostasis.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2025 Jul 10;24(1):272. doi: 10.1186/s12933-025-02801-w. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2025. PMID: 40640752 Free PMC article.
-
Oxidized LDL stimulates PKM2-mediated mtROS production and phagocytosis.J Lipid Res. 2025 May;66(5):100809. doi: 10.1016/j.jlr.2025.100809. Epub 2025 Apr 16. J Lipid Res. 2025. PMID: 40250804 Free PMC article.
-
Menaquinone-4 inhibits the formation and vulnerability of atherosclerotic plaques in apolipoprotein E knockout mice by decreasing the uptake of the oxidized low-density lipoprotein in macrophages.Eur J Pharmacol. 2025 Sep 15;1003:177970. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2025.177970. Epub 2025 Jul 17. Eur J Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40683443
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Human CD36: Gene Regulation, Protein Function, and Its Role in Atherosclerosis Pathogenesis.Genes (Basel). 2025 Jun 13;16(6):705. doi: 10.3390/genes16060705. Genes (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40565598 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Adada M., Luberto C., Canals D. Inhibitors of the sphingomyelin cycle: sphingomyelin synthases and sphingomyelinases. Chem. Phys. Lipids. 2016;197:45–59. - PubMed
-
- Isik O.A., Cizmecioglu O. Rafting on the plasma membrane: lipid rafts in signaling and disease. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2023;1436:87–108. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

