Role of inflammation in depressive and anxiety disorders, affect, and cognition: genetic and non-genetic findings in the lifelines cohort study
- PMID: 40348744
- PMCID: PMC12065825
- DOI: 10.1038/s41398-025-03372-w
Role of inflammation in depressive and anxiety disorders, affect, and cognition: genetic and non-genetic findings in the lifelines cohort study
Erratum in
-
Correction: Role of inflammation in depressive and anxiety disorders, affect, and cognition: genetic and non-genetic findings in the lifelines cohort study.Transl Psychiatry. 2025 Oct 29;15(1):437. doi: 10.1038/s41398-025-03713-9. Transl Psychiatry. 2025. PMID: 41152245 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
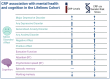
Inflammation is associated with a range of neuropsychiatric symptoms, but the issue of causality remains unclear. We used complementary non-genetic, genetic risk score (GRS), and Mendelian randomization (MR) analyses to examine whether inflammatory markers are associated with affect, depressive and anxiety disorders, and cognition. We tested in ≈55,098 (59% female) individuals from the Dutch Lifelines cohort the concurrent/prospective associations of C-reactive protein (CRP) with: depressive and anxiety disorders; positive/negative affect; and attention, psychomotor speed, episodic memory, and executive functioning at baseline and a follow-up assessment occurring 3.91 years later (SD = 1.21). Additionally, we examined the association between inflammatory GRSs (CRP, interleukin-6 [IL-6], IL-6 receptor [IL-6R and soluble IL-6R (sIL-6R)], glycoprotein acetyls [GlycA]) on these same outcomes (Nmin = 35,300; Nmax = 57,946), followed by MR analysis examining evidence of causality of CRP on outcomes (Nmin=22,154; Nmax = 23,268). In non-genetic analyses, higher CRP was associated with depressive disorder, lower positive/higher negative affect, and worse executive function, attention, and psychomotor speed after adjusting for potential confounders. In genetic analyses, CRPGRS was associated with any anxiety disorder (β = 0.002, p = 0.037) whereas GlycAGRS was associated with major depressive disorder (β = 0.001, p = 0.036). Both CRPGRS (β = 0.006, p = 0.035) and GlycAGRS (β = 0.006, p = 0.049) were associated with greater negative affect. Inflammatory GRSs were not associated with cognition, except sIL-6RGRS which was associated with poorer memory (β = -0.009, p = 0.018). There was a non-significant CRP-anxiety association using MR (β = 0.12; p = 0.054). Genetic and non-genetic analyses provide consistent evidence for an association between CRP and negative affect. These results suggest that inflammation may impact a broad range of trans-diagnostic affective symptoms.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Update of
-
Role of Inflammation in Depressive and Anxiety Disorders, Affect, and Cognition: Genetic and Non-Genetic Findings in the Lifelines Cohort Study.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Apr 19:2024.04.17.24305950. doi: 10.1101/2024.04.17.24305950. medRxiv. 2024. Update in: Transl Psychiatry. 2025 May 10;15(1):164. doi: 10.1038/s41398-025-03372-w. PMID: 38699368 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Role of Inflammation in Depressive and Anxiety Disorders, Affect, and Cognition: Genetic and Non-Genetic Findings in the Lifelines Cohort Study.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2024 Aug 10:rs.3.rs-4379779. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-4379779/v1. Res Sq. 2024. Update in: Transl Psychiatry. 2025 May 10;15(1):164. doi: 10.1038/s41398-025-03372-w. PMID: 39149475 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- James SL, Abate D, Abate KH, Abay SM, Abbafati C, Abbasi N, et al. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 354 diseases and injuries for 195 countries and territories, 1990–2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet. 2018;392:1789–858. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

