Real world study on efficacy and safety of surufatinib in advanced solid tumors evaluation
- PMID: 40348748
- PMCID: PMC12065879
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-00974-8
Real world study on efficacy and safety of surufatinib in advanced solid tumors evaluation
Abstract
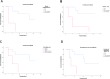
Surufatinib is a novel, China-developed small-molecule tyrosine kinase inhibitor that demonstrates high selectivity for VEGFR, FGFR1, and CSF1R. Surufatinib has been approved for the treatment of neuroendcrine tumors, including pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors (PNEN) and non-pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors (N-pNEN). The purpose of this retrospective study is to assess Surufatinib's safety and effectiveness in patients with various advanced solid malignancies. The general clinical statistics and follow-up data of patients treated with Surufatinib for advanced solid tumors at Zhejiang Provincial People's Hospital between January 2021 and April 2024 were gathered. Enhanced CT was used to assess the effectiveness during that time, and cases side effects were gathered. Survival rates of different diseases were analyzed using the Kaplan-Meier method. A total of 28 eligible patients were enrolled in this study. At the end of follow-up, treatment with Surufatinib resulted in the following outcomes: Complete response (CR) in 0 cases (0.0%), Partial response (PR) in 5 cases (17.9%), Stable disease (SD) in 7 cases (25.0%), and Progressive disease (PD) in 16 cases (57.1%). Objective response rate (ORR) and Disease control rate (DCR) were 17.9% and 42.9%, respectively. In the PNEN group, ORR was 33.3%, DCR was 66.7%, median progression-free survival (mPFS) was 11 months, while median overall survival (mOS) was 17 months. In the N-pNEN group, ORR was 14.3%, DCR was 42.3%, mPFS was 6 months and mOS was 7 months. ORR was 8.3%, DCR was 25%, mPFS was 2 months, and mOS was 2 months. The most common adverse reactions included hypoproteinemia, proteinuria, bone marrow suppression and gastrointestinal toxicity, and which of them were grade 1 to grade 2. In advanced solid tumors beyond PNEN, Surufatinib demonstrates clinically meaningful survival benefits for patients refractory to standard therapies, with a generally manageable safety profile.
Keywords: Non-pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor; Pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor; Solid tumor; Surufatinib; Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Informed consent: Confirms that informed consent was obtained from all participants and their legal guardians. Institutional review board: This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Zhejiang Provincial People’s Hospital. Confirms that all experiments were performed in accordance with relevant named guidelines and regulations.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

