Mapping the interaction surface between CaVβ and actin and its role in calcium channel clearance
- PMID: 40348749
- PMCID: PMC12065904
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-59548-x
Mapping the interaction surface between CaVβ and actin and its role in calcium channel clearance
Abstract
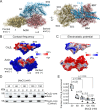
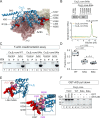
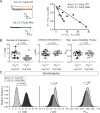
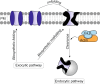
Defective ion channel turnover and clearance of damaged proteins are associated with aging and neurodegeneration. The L-type CaV1.2 voltage-gated calcium channel mediates depolarization-induced calcium signals in heart and brain. Here, we determined the interaction surface between actin and two calcium channel subunits, CaVβ2 and CaVβ4, using cross-linking mass spectrometry and protein-protein docking, and uncovered a role in replenishing conduction-defective CaV1.2 channels. Computational and in vitro mutagenesis identified hotspots in CaVβ that decreased the affinity for actin but not for CaV1.2. When coexpressed with CaV1.2, none of the tested actin-association-deficient CaVβ mutants altered the single-channel properties or the total number of channels at the cell surface. However, coexpression with the CaVβ2 hotspot mutant downregulated current amplitudes, and with a concomitant reduction in the number of functionally available channels, indicating that current inhibition resulted from a build-up of conduction silent channels. Our findings established CaVβ2-actin interaction as a key player for clearing the plasma membrane of corrupted CaV1.2 proteins to ensure the maintenance of a functional pool of channels and proper calcium signal transduction. The CaVβ-actin molecular model introduces a potentially druggable protein-protein interface to intervene CaV-mediated signaling processes.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Direct interaction of CaVβ with actin up-regulates L-type calcium currents in HL-1 cardiomyocytes.J Biol Chem. 2015 Feb 20;290(8):4561-4572. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.573956. Epub 2014 Dec 22. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25533460 Free PMC article.
-
Functional properties of the CaV1.2 calcium channel activated by calmodulin in the absence of alpha2delta subunits.Channels (Austin). 2009 Jan-Feb;3(1):25-31. doi: 10.4161/chan.3.1.7498. Epub 2009 Jan 25. Channels (Austin). 2009. PMID: 19106618 Free PMC article.
-
Engineering selectivity into RGK GTPase inhibition of voltage-dependent calcium channels.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018 Nov 20;115(47):12051-12056. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1811024115. Epub 2018 Nov 5. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018. PMID: 30397133 Free PMC article.
-
L-type CaV1.2 calcium channels: from in vitro findings to in vivo function.Physiol Rev. 2014 Jan;94(1):303-26. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00016.2013. Physiol Rev. 2014. PMID: 24382889 Review.
-
Structure-Function Relationship of the Voltage-Gated Calcium Channel Cav1.1 Complex.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;981:23-39. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-55858-5_2. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017. PMID: 29594856 Review.
References
-
- Hidalgo, P. & Neely, A. Multiplicity of protein interactions and functions of the voltage-gated calcium channel β-subunit. Cell calcium42, 389–396 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Rima, M. et al. Protein partners of the calcium channel β-subunit highlight new cellular functions. Biochemical J.473, 1831–1844 (2016). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

