The profile of gastrointestinal dysfunction in prodromal to late-stage Parkinson's disease
- PMID: 40348767
- PMCID: PMC12065915
- DOI: 10.1038/s41531-025-00900-9
The profile of gastrointestinal dysfunction in prodromal to late-stage Parkinson's disease
Abstract
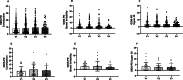
Gastrointestinal dysfunction (GID) may play a key role in Parkinson's disease (PD) but its relationship with disease progression remains unclear. We recruited 404 PD cases, 37 iRBD (isolated REM Sleep Behaviour Disorder) and 105 controls. Participants completed the Gastrointestinal Dysfunction Scale for PD (GIDS-PD) and standardised disease severity assessments. Whole gut transit time (WGTT) was measured by ingestion of blue dye and recorded time to blue stools appearance ('Blue Poop Challenge') in a subset of PD cases. Gastrointestinal symptoms were more common and prevalent in iRBD and PD versus controls, and WGTT was significantly higher in PD versus controls. After adjustment for confounding factors, disease stage was not a significant predictor of GIDS-PD Constipation or Bowel Irritability scores. Longitudinal assessment of GIDS-PD scores and WGTT confirmed stability over a 4 year period. Bowel dysfunction may be a phenotypic feature in a subset of Parkinson's with implications for patient stratification and management.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Dilmaghani, S. et al. Severity of dysphagia is associated with hospitalizations and mortality in patients with Parkinson’s disease. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 34, 10.1111/nmo.14280 (2022). - PubMed
-
- Krogh, K., Ostergaard, K., Sabroe, S. & Laurberg, S. Clinical aspects of bowel symptoms in Parkinson’s disease. Acta Neurol. Scand.117, 60–64 (2008). - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

