A minimally invasive thrombotic model to study stroke in awake mice
- PMID: 40348793
- PMCID: PMC12065827
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-59617-1
A minimally invasive thrombotic model to study stroke in awake mice
Abstract
Experimental stroke models in rodents are essential for mechanistic studies and therapeutic development. However, these models have several limitations negatively impacting their translational relevance. Here we aimed to develop a minimally invasive thrombotic stroke model through magnetic particle delivery that does not require craniotomy, is amenable to reperfusion therapy, can be combined with in vivo imaging modalities, and can be performed in awake mice. We found that the model results in reproducible cortical infarcts within the middle cerebral artery (MCA) territory with cytologic and immune changes similar to that observed with more invasive distal MCA occlusion models. Importantly, the injury produced by the model was ameliorated by tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) administration. We also show that MCA occlusion in awake animals results in bigger ischemic lesions independent of day/night cycle. Magnetic particle delivery had no overt effects on physiologic parameters and systemic immune biomarkers. In conclusion, we developed a novel stroke model in mice that fulfills many requirements for modeling human stroke.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: C.I. serves on the scientific advisory board of Broadview Ventures. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

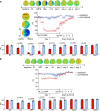
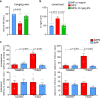
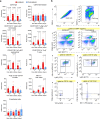
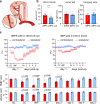
Update of
-
A minimally invasive thrombotic stroke model to study circadian rhythm in awake mice.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jun 18:2024.06.10.598243. doi: 10.1101/2024.06.10.598243. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Nat Commun. 2025 May 10;16(1):4356. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-59617-1. PMID: 38915621 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Virani, S. S. et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics—2020 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation141, e139–e596 (2020). - PubMed
-
- Campbell, B. C. V. et al. Ischaemic stroke. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim.5, 70 (2019). - PubMed
-
- Virani, S. S. et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics—2021 update. Circulation143, e254–e743 (2021). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 NS081179/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- NS081179/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS)
- P30 CA008748/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- StrokeIMPaCT/Fondation Leducq
- NS132493/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

