Molecular mechanisms of viral oncogenesis in haematological malignancies: perspectives from metabolic reprogramming, epigenetic regulation and immune microenvironment remodeling
- PMID: 40349096
- PMCID: PMC12065340
- DOI: 10.1186/s40164-025-00655-2
Molecular mechanisms of viral oncogenesis in haematological malignancies: perspectives from metabolic reprogramming, epigenetic regulation and immune microenvironment remodeling
Abstract
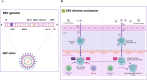
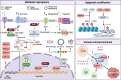
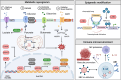
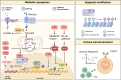
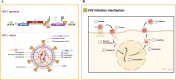
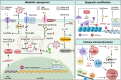
Haematological malignancies are one of the most common tumors, with a rising incidence noted over recent decades. Viral infections play significant roles in the pathogenesis of these malignancies globally. This review delves into the contributions of various known viruses-specifically Epstein-Barr virus (EBV), human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 (HTLV-1), Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV), human cytomegalovirus (HCMV), hepatitis B virus (HBV), hepatitis C virus (HCV), and human papillomavirus (HPV)-in the development of haematological malignancies. These viruses are shown to drive tumorigenesis through mechanisms, such as metabolic reprogramming, epigenetic modifications, and remodeling of the immune microenvironment. By directly disrupting fundamental cellular functions and altering metabolic and epigenetic pathways, these viruses foster an immune milieu that supports both viral persistence and tumor growth. A thorough understanding of these viral oncogenic processes is crucial not only for etiological discovery but also for developing targeted interventions. This review emphasizes the need for continued research into the specific ways these viruses manipulate the host cell's metabolic and epigenetic environments, aiming to provide insights that could guide future advancements in treatment modalities.
Keywords: Epigenetic regulation; Haematological malignancies; Immune microenvironment; Metabolism; Oncogenic viruses.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
- 2024JXJL-YFX0022/Special Project for Performance Incentive Guidance of Scientific Research Institutions
- CSTB2022NSCQ-MSX1150/the Natural Science Foundation of Chongqing, China
- 2022CDJYGRH-001/the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities
- cstc2022ycjh-bgzxm0048/the Chongqing Professional Talents Plan
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

