Ultrasound-based deep learning radiomics for enhanced axillary lymph node metastasis assessment: a multicenter study
- PMID: 40349137
- PMCID: PMC12065944
- DOI: 10.1093/oncolo/oyaf090
Ultrasound-based deep learning radiomics for enhanced axillary lymph node metastasis assessment: a multicenter study
Abstract
Background: Accurate preoperative assessment of axillary lymph node metastasis (ALNM) in breast cancer is crucial for guiding treatment decisions. This study aimed to develop a deep-learning radiomics model for assessing ALNM and to evaluate its impact on radiologists' diagnostic accuracy.
Methods: This multicenter study included 866 breast cancer patients from 6 hospitals. The data were categorized into training, internal test, external test, and prospective test sets. Deep learning and handcrafted radiomics features were extracted from ultrasound images of primary tumors and lymph nodes. The tumor score and LN score were calculated following feature selection, and a clinical-radiomics model was constructed based on these scores along with clinical-ultrasonic risk factors. The model's performance was validated across the 3 test sets. Additionally, the diagnostic performance of radiologists, with and without model assistance, was evaluated.
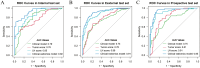
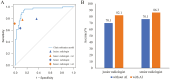
Results: The clinical-radiomics model demonstrated robust discrimination with AUCs of 0.94, 0.92, 0.91, and 0.95 in the training, internal test, external test, and prospective test sets, respectively. It surpassed the clinical model and single score in all sets (P < .05). Decision curve analysis and clinical impact curves validated the clinical utility of the clinical-radiomics model. Moreover, the model significantly improved radiologists' diagnostic accuracy, with AUCs increasing from 0.71 to 0.82 for the junior radiologist and from 0.75 to 0.85 for the senior radiologist.
Conclusions: The clinical-radiomics model effectively predicts ALNM in breast cancer patients using noninvasive ultrasound features. Additionally, it enhances radiologists' diagnostic accuracy, potentially optimizing resource allocation in breast cancer management.
Keywords: axillary lymph node metastasis; breast cancer; predictive model; radiomics; ultrasound.
© The Author(s) 2025. Published by Oxford University Press.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing or financial interests.
Figures

References
-
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, et al.Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71:209-249. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21660 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Park KU, Caudle A.. Management of the axilla in the patient with breast cancer. Surg Clin North Am. 2018;98:747-760. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.suc.2018.04.001 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Tamirisa N, Thomas SM, Fayanju OM, et al.Axillary nodal evaluation in elderly breast cancer patients: potential effects on treatment decisions and survival. Ann Surg Oncol. 2018;25:2890-2898. https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-018-6595-2 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chang JM, Leung JWT, Moy L, Ha SM, Moon WK.. Axillary nodal evaluation in breast cancer: state of the art. Radiology. 2020;295:500-515. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2020192534 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Yu Y, He Z, Ouyang J, et al.Magnetic resonance imaging radiomics predicts preoperative axillary lymph node metastasis to support surgical decisions and is associated with tumor microenvironment in invasive breast cancer: a machine learning, multicenter study. EBioMedicine. 2021;69:103460. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ebiom.2021.103460 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

