Stearoyl-CoA desaturase 1 deficiency drives saturated lipid accumulation and increases liver and plasma acylcarnitines
- PMID: 40350036
- PMCID: PMC12173144
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jlr.2025.100824
Stearoyl-CoA desaturase 1 deficiency drives saturated lipid accumulation and increases liver and plasma acylcarnitines
Abstract
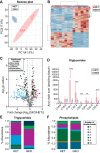
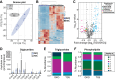
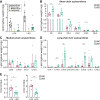
Stearoyl-CoA desaturase-1 (SCD1) is a critical regulator of lipogenesis that catalyzes the synthesis of MUFAs, mainly oleate (18:1n-9) and palmitoleate (16:1n-7) from saturated fatty acids, stearoyl-CoA (18:0) and palmitoyl-CoA (16:0), respectively. Elevated SCD1 expression and its products are associated with obesity, metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease, insulin resistance, and cancer. Conversely, Scd1 deficiency diminishes de novo lipogenesis and protects mice against adiposity, hepatic steatosis, and hyperglycemia. Yet, the comprehensive impact of Scd1 deficiency on hepatic and circulating lipids remains incompletely understood. To further delineate the effects of SCD1 on lipid metabolism, we employed lipidomics on the liver from mice under a lipogenic high carbohydrate, very low-fat diet. We found that Scd1 deficiency leads to an accumulation of saturated lipids and an increase in hepatic and plasma acylcarnitines. Remarkably, transgenic replenishment of de novo oleate synthesis by human SCD5 in the liver of Scd1-deficient mice not only restored hepatic lipid desaturation levels but also attenuated acylcarnitine accumulation, highlighting the distinct role of SCD1 and oleate in regulating intracellular lipid homeostasis.
Keywords: SCD1; SCD5; acylcarnitines; lipidomics; oleate; saturated fatty acid.
Copyright © 2025 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest The author declares that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article.
Figures



References
-
- Miyazaki M., Flowers M.T., Sampath H., Chu K., Otzelberger C., Liu X., et al. Hepatic stearoyl-CoA desaturase-1 deficiency protects mice from carbohydrate-induced adiposity and hepatic steatosis. Cell Metab. 2007;6:484–496. - PubMed
-
- Miyazaki M., Ntambi J.M. Role of stearoyl-coenzyme A desaturase in lipid metabolism. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fatty Acids. 2003;68:113–121. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

