Unraveling cysteinyl leukotrienes and their receptors in inflammation through the brain-gut-lung axis
- PMID: 40351036
- PMCID: PMC12077450
- DOI: 10.1080/21505594.2025.2502555
Unraveling cysteinyl leukotrienes and their receptors in inflammation through the brain-gut-lung axis
Abstract
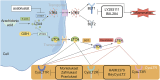
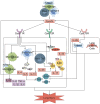
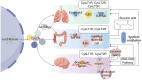
Cysteinyl leukotrienes (CysLTs), as potent lipid inflammatory mediators, play a pivotal role in systemic multi-organ inflammation and inter-organ communication through interactions with their receptors (CysLTRs). However, However, the function of CysLT3R is unclear and lacks a network of cross-organ metabolite interactions, and the clinical use of leukotriene receptor antagonists (LTRAs) has certain limitations. This review systematically synthesizes existing evidence and proposes future directions by clarifying receptor subtype specificity, optimizing targeted therapies, exploring CysLTs' applications in neuroimmunology, and elucidating the dual roles of CysLTs in chronic inflammation. It is indicated that CysLTs activate eosinophils, mast cells, and airway tuft cells, driving type 2 immune responses and mucus secretion in the lungs, thereby exacerbating respiratory diseases such as asthma. In the nervous system, CysLTs aggravate neurodegenerative disorders like cerebral ischemia and Alzheimer's disease by disrupting the blood-brain barrier, promoting glial activation, and inducing neuronal damage. In the gut, CysLTs regulate anti-helminth immunity via the tuft cell-ILC2 pathway and collaborate with prostaglandin D2 (PGD2) to modulate bile excretion and mucosal protection. Furthermore, CysLTs mediate communication through the gut-lung and gut-brain axes via metabolites such as succinate, contributing to cross-organ inflammatory regulation. In conclusion, this review highlights the complex roles of CysLTs in chronic inflammation, providing a theoretical foundation for precise intervention in multi-organ inflammatory diseases, which provides a theoretical framework for precision interventions in multi-organ inflammatory diseases and inspires interdisciplinary breakthroughs.
Keywords: Cysteinyl; gut-brain axis; gut-lung axis; inflammation; leukotriene.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures
Similar articles
-
Leukotrienes: Bridging the Inflammatory Gap in Asthma and Inflammatory Bowel Diseases (IBD).Compr Physiol. 2025 Jun;15(3):e70022. doi: 10.1002/cph4.70022. Compr Physiol. 2025. PMID: 40568744 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cysteinyl Leukotrienes in Allergic Inflammation.Annu Rev Pathol. 2025 Jan;20(1):115-141. doi: 10.1146/annurev-pathmechdis-111523-023509. Epub 2025 Jan 2. Annu Rev Pathol. 2025. PMID: 39374430 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Guidelines for the prevention and management of bronchial asthma (2024 edition)].Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi. 2025 Mar 12;48(3):208-248. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112147-20241013-00601. Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi Za Zhi. 2025. PMID: 40050074 Chinese.
-
Montelukast in the treatment of allergic rhinitis: an evidence-based review.Drugs. 2007;67(6):887-901. doi: 10.2165/00003495-200767060-00005. Drugs. 2007. PMID: 17428106
-
Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome.2025 Jun 20. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 Jun 20. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 31613449 Free Books & Documents.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
