Tissue eosinophil level as a predictor of control, severity, and recurrence of Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps
- PMID: 40351330
- PMCID: PMC12061883
- DOI: 10.3389/falgy.2025.1549332
Tissue eosinophil level as a predictor of control, severity, and recurrence of Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps
Abstract
Introduction: The histopathologic study of nasal polyps establishes endotype features of chronic rhinosinusitis (CRS). A tissular eosinophil count greater than 10 per high power field (HPF) classifies this condition as type 2 inflammation. Blood and mucosal eosinophils are suggested as biomarkers of severity and control of CRS. Additionally, a tissular eosinophil count greater than 55 per HPF has been related to a high risk of recurrence in the Asian population. Our study aims to determine whether tissue eosinophil count is associated with the control, severity, and recurrence of Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps (CRSwNP).
Methods: An observational study of patients with CRSwNP who underwent nasal mucosa biopsy was conducted between June 2021 and November 2023. Histopathologic features, asthma control, CRSwNP control and severity according to the POLINA consensus, quality of life parameters, recurrence of CRSwNP, and laboratory markers were recorded and compared with the tissular eosinophil count.
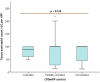
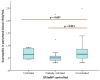
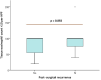
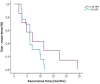
Results: A total of 108 cases were included. The majority (70.4%) had concomitant asthma, with 31.5% of the cases having well-controlled disease. Most patients had uncontrolled (57.4%) and severe (62%) CRSwNP. Fifty-four cases underwent surgery and 43.5% experienced recurrence. More than half had a SNOT-22 score greater than 50 points. Eighty-one percent of patients had a tissular eosinophil count greater than 10 per HPF, and 60.2% had blood eosinophilia greater than . Blood eosinophilia was related to CRSwNP severity and control. No significant differences were found between tissue eosinophil count and the severity, control, and recurrence of CRSwNP.
Conclusion: Tissue eosinophil levels were not a marker of control, severity, and recurrence of CRSwNP in our data. Blood eosinophil levels, however, were a marker of CRSwNP control and severity.
Keywords: Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps; biomarkers; disease control; eosinophilic inflammation; recurrence; tissue eosinophilia; type 2 inflammation.
© 2025 Vizcarra-Melgar, Sánchez-Gómez, López-González, Moreno-Luna, González-García and Maza-Solano.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Comment in
-
Commentary: Tissue eosinophil level as a predictor of control, severity, and recurrence of Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps.Front Allergy. 2025 Jun 26;6:1628864. doi: 10.3389/falgy.2025.1628864. eCollection 2025. Front Allergy. 2025. PMID: 40642608 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Systemic and topical antibiotics for chronic rhinosinusitis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Apr 26;4(4):CD011994. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011994.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27113482 Free PMC article.
-
Equivalent healthcare resource use following either a long-acting steroid-eluting implant or repeat endoscopic surgery for chronic rhinosinusitis patients with nasal polyp recurrence: a real-world evidence study.Curr Med Res Opin. 2025 May;41(5):767-777. doi: 10.1080/03007995.2025.2513955. Epub 2025 Jun 11. Curr Med Res Opin. 2025. PMID: 40478176
-
Intranasal steroids versus placebo or no intervention for chronic rhinosinusitis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 Apr 26;4(4):CD011996. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011996.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 27115217 Free PMC article.
-
Oral and intranasal aspirin desensitisation for non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID)-exacerbated respiratory disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2025 Jan 7;1(1):CD013476. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013476.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2025. PMID: 39775459
-
Aberrant expression of Bcl2L12 as a potential biomarker for predicting recurrence in nasal polyp.Braz J Otorhinolaryngol. 2025 Jul 4;91(5):101670. doi: 10.1016/j.bjorl.2025.101670. Online ahead of print. Braz J Otorhinolaryngol. 2025. PMID: 40617234 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Commentary: Tissue eosinophil level as a predictor of control, severity, and recurrence of Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps.Front Allergy. 2025 Jun 26;6:1628864. doi: 10.3389/falgy.2025.1628864. eCollection 2025. Front Allergy. 2025. PMID: 40642608 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

