Current Management of Neurological Wilson's Disease
- PMID: 40351566
- PMCID: PMC12063596
- DOI: 10.5334/tohm.938
Current Management of Neurological Wilson's Disease
Abstract
Wilson's disease (WD) is a disorder of copper metabolism due to variants in the ATP7B gene. This autosomal recessively inherited disorder is characterized by the accumulation of copper in various body parts, mainly the liver, brain, and kidneys. Initially, WD was described to involve the hepatic and neurological systems. Subsequently, diverse presentations have been reported with skeletal and hematological manifestations and various constellations of symptoms. Neurological manifestations of WD are varied, ranging from asymptomatic neurological state to refractory dystonia. Earlier, the diagnosis was based only on measuring serum ceruloplasmin levels, urinary copper levels, and imaging. Advanced genetic testing has provided an additional mode of diagnosis in the patient, screening of the family members and, a way to better understand the genotype-phenotype associations of the disease if there are any. In the last few decades, the treatment of WD has evolved from symptomatic treatment and chelation therapy to many new advanced measures for both copper chelation and symptomatic relief. With a better understanding of the genetic aspects of WD in recent years, there has been more focus on gene therapy, novel therapies targeting ATP7B genes, and therapies targeting mutant proteins to prevent copper accumulation. This article highlights the advances in diagnostic methods and treatment modalities in WD.
Keywords: Movement disorders; Neurological and/or hepatic WD; Outcome; Treatment; Wilson’s disease.
Copyright: © 2025 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no competing interests to declare.
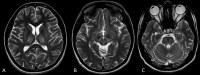
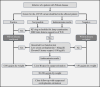
Figures

References
-
- Kasztelan-Szczerbinska B, Cichoz-Lach H. Wilson’s Disease: An Update on the Diagnostic Workup and Management. J Clin Med [Internet]. 2021. [cited 2024 May 24];10. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34768617/. DOI: 10.3390/jcm10215097 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Alkhouri N, Gonzalez-Peralta RP, Medici V. Wilson disease: a summary of the updated AASLD Practice Guidance. Hepatol Commun [Internet]. 2023. [cited 2025 Feb 2];7. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37184530/. DOI: 10.1097/HC9.0000000000000150 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chu NS, Hung TP. Geographic variations in Wilson’s disease. J Neurol Sci [Internet]. 1993. [cited 2024 May 24];117:1–7. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/8410043/. DOI: 10.1016/0022-510X(93)90145-O - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

