A new quantum-inspired pattern based on Goldner-Harary graph for automated alzheimer's disease detection
- PMID: 40351570
- PMCID: PMC12065701
- DOI: 10.1007/s11571-025-10249-7
A new quantum-inspired pattern based on Goldner-Harary graph for automated alzheimer's disease detection
Abstract
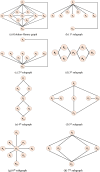
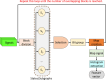
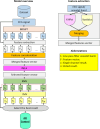
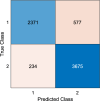
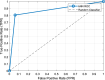
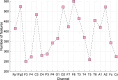
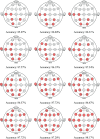
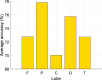
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a common cause of dementia. We aimed to develop a computationally efficient yet accurate feature engineering model for AD detection based on electroencephalography (EEG) signal inputs. New method: We retrospectively analyzed the EEG records of 134 AD and 113 non-AD patients. To generate multilevel features, a multilevel discrete wavelet transform was used to decompose the input EEG-signals. We devised a novel quantum-inspired EEG-signal feature extraction function based on 7-distinct different subgraphs of the Goldner-Harary pattern (GHPat), and selectively assigned a specific subgraph, using a forward-forward distance-based fitness function, to each input EEG signal block for textural feature extraction. We extracted statistical features using standard statistical moments, which we then merged with the extracted textural features. Other model components were iterative neighborhood component analysis feature selection, standard shallow k-nearest neighbors, as well as iterative majority voting and greedy algorithm to generate additional voted prediction vectors and select the best overall model results. With leave-one-subject-out cross-validation (LOSO CV), our model attained 88.17% accuracy. Accuracy results stratified by channel lead placement and brain regions suggested P4 and the parietal region to be the most impactful. Comparison with existing methods: The proposed model outperforms existing methods by achieving higher accuracy with a computationally efficient quantum-inspired approach, ensuring robustness and generalizability. Cortex maps were generated that allowed visual correlation of channel-wise results with various brain regions, enhancing model explainability.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Brain-computer interface; EEG; GHPat; Goldner-Harary graph; Signal classification.
© The Author(s) 2025.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Primate brain pattern-based automated Alzheimer's disease detection model using EEG signals.Cogn Neurodyn. 2023 Jun;17(3):647-659. doi: 10.1007/s11571-022-09859-2. Epub 2022 Aug 12. Cogn Neurodyn. 2023. PMID: 37265658 Free PMC article.
-
Lattice 123 pattern for automated Alzheimer's detection using EEG signal.Cogn Neurodyn. 2024 Oct;18(5):2503-2519. doi: 10.1007/s11571-024-10104-1. Epub 2024 Apr 3. Cogn Neurodyn. 2024. PMID: 39555305 Free PMC article.
-
Multilevel hybrid accurate handcrafted model for myocardial infarction classification using ECG signals.Int J Mach Learn Cybern. 2023;14(5):1651-1668. doi: 10.1007/s13042-022-01718-0. Epub 2022 Nov 28. Int J Mach Learn Cybern. 2023. PMID: 36467277 Free PMC article.
-
ChMinMaxPat: Investigations on Violence and Stress Detection Using EEG Signals.Diagnostics (Basel). 2024 Nov 26;14(23):2666. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics14232666. Diagnostics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39682574 Free PMC article.
-
Black-white hole pattern: an investigation on the automated chronic neuropathic pain detection using EEG signals.Cogn Neurodyn. 2024 Oct;18(5):2193-2210. doi: 10.1007/s11571-024-10078-0. Epub 2024 Feb 28. Cogn Neurodyn. 2024. PMID: 39555288 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abedinzadeh Torghabeh F, Hosseini SA, Modaresnia Y (2023) Potential biomarker for early detection of ADHD using phase-based brain connectivity and graph theory. Phys Eng Sci Med 46(4):1447–1465 - PubMed
-
- Acharya M, Deo RC, Barua PD, Devi A, Tao X (2025) EEGConvNeXt: a novel convolutional neural network model for automated detection of Alzheimer’s disease and frontotemporal dementia using EEG signals. Comput Methods Prog Biomed 262:108652. 10.1016/j.cmpb.2025.108652 - PubMed
-
- Arjmandi-Rad S, Vestergaard Nieland JD, Goozee KG, Vaseghi S (2024) The effects of different acetylcholinesterase inhibitors on EEG patterns in patients with Alzheimer’s disease: A systematic review. Neurol Sci 45(2):417–430 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

