EuleApp©: a computerized adaptive assessment tool for early literacy skills
- PMID: 40351601
- PMCID: PMC12062173
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2025.1522740
EuleApp©: a computerized adaptive assessment tool for early literacy skills
Abstract
Introduction: Ample evidence indicates that assessing children's early literacy skills is crucial for later academic success. This assessment enables the provision of necessary support and materials while engaging them in the culture of print and books before school entry. However, relatively few assessment tools are available to identify early literacy skills, such as concepts of print, print awareness, phonological awareness, word awareness, alphabet knowledge, and early reading. The digital landscape presents new opportunities to enhance these assessments and provide enriching early literacy experiences. This study examines the psychometric properties of an adaptive assessment tool, EuLeApp©, focusing on its reliability and concurrent validity.
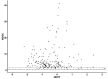
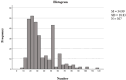
Methods: Data involved 307 German kindergarten children (Mage = 64 months old, range = 45-91). A Computerized Adaptive Testing (CAT) method, grounded in Item Response Theory (IRT), was employed to develop an adaptive digital tool for assessing early literacy competencies. We utilized an automatic item selection procedure based on item difficulty and discrimination parameters for the 183-item pool to ensure a precise and efficient assessment tailored to each child's ability level.
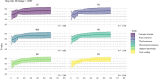
Results: The 4-parameter Logistic (4PL) model was identified as the best-fitting model for adaptive assessment, providing the highest precision in estimating children's abilities within this framework.
Discussions: The findings support the idea that the adaptive digital-based assessment tool EuLeApp© can be used to assess early literacy skills. It also provides a foundation for offering individualized and adaptable learning opportunities embedded in daily routines in daycare centers.
Keywords: computerized adaptive test; digital assessment; early literacy; item response theory; preschool age; psychometric validation.
Copyright © 2025 Yumus, Stuhr, Meindl, Leuschner and Jungmann.
Conflict of interest statement
HL is the founder of DHL Data Science Seminars. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Ackerman T. A., Gierl M. J., Walker C. M. (2003). Using multidimensional item response theory to evaluate educational and psychological tests. Educ. Meas. Issues Pract. 22, 37–51. doi: 10.1111/j.1745-3992.2003.tb00136.x - DOI
-
- Adams M. J. (1994). Beginning to read: Thinking and learning about print.
-
- Antoniou F., Ralli A. M., Mouzaki A., Diamanti V., Papaioannou S. (2022). Logometro®: the psychometric properties of a norm-referenced digital battery for language assessment of Greek-speaking 4–7 years old children. Front. Psychol. 13:900600. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.900600, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Anderson V., Levin H. S., Jacobs R. (2002). Executive functions after frontal lobe injury: A developmental perspective. J. Clin. Exp. Neuropsychol. 24, 224–247. doi: 10.1207/S15327647JCD1201_02 - DOI
-
- Baker F. (2001). The basics of item response theory: ERIC clearinghouse on assessment and evaluation. College Park, MD: University of Maryland, ERIC Clearinghouse on Assessment and Evaluation.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

