The cGAS-STING pathway in atherosclerosis
- PMID: 40351606
- PMCID: PMC12062000
- DOI: 10.3389/fcvm.2025.1550930
The cGAS-STING pathway in atherosclerosis
Erratum in
-
Correction: The cGAS-STING pathway in atherosclerosis.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2025 Jun 20;12:1641100. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2025.1641100. eCollection 2025. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2025. PMID: 40621068 Free PMC article.
Abstract
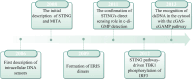
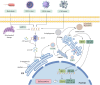
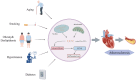
Atherosclerosis (AS), a chronic inflammatory disease, remains a leading contributor to cardiovascular morbidity and mortality. Recent studies highlight the critical role of the cGAS-STING pathway-a key innate immune signaling cascade-in driving AS progression. This pathway is activated by cytoplasmic DNA from damaged cells, thereby triggering inflammation and accelerating plaque formation. While risk factors such as aging, obesity, smoking, hypertension, and diabetes are known to exacerbate AS, emerging evidence suggests that these factors may also enhance cGAS-STING pathway, which amplifies inflammatory responses. Targeting this pathway offers a promising therapeutic strategy to reduce the burden of cardiovascular diseases (CVD). In this review, we summarize the mechanisms of the cGAS-STING pathway, explore its role in AS, and evaluate potential inhibitors as future therapeutic candidates. By integrating current knowledge, we aim to provide insights for developing novel treatments to mitigate AS and CVD burden.
Keywords: STING inhibitors; atherosclerosis; cGAS inhibitors; cGAS-STING pathway; risk factors; therapeutic potential.
© 2025 Wang, Chen, Jin and Bilal.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

