A Rare Case of Bilateral Xanthomatosis of Tendon of Achilles: A Case Report
- PMID: 40351640
- PMCID: PMC12064235
- DOI: 10.13107/jocr.2025.v15.i05.5562
A Rare Case of Bilateral Xanthomatosis of Tendon of Achilles: A Case Report
Abstract
Introduction: Xanthomatosis is an atypical pseudotumor of connective tissue characterized by the accumulation of lipid-laden histiocytes, often manifesting as encapsulated yellowish masses. It is commonly associated with familial hypercholesterolemia (FH). This case report aims to present a rare instance of bilateral xanthomatosis affecting the Achilles tendons in a 42-year-old male, which underscores the importance of identifying clinical and radiological findings of this condition to facilitate early diagnosis and intervention for related musculoskeletal and metabolic disorders.
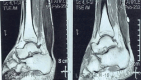
Case report: A 42-year-old male presented with a 6-year history of asymptomatic swelling in the distal aspect of both legs. On examination, firm, non-tender, non-reducible, and non-mobile masses were observed without signs of inflammation, and the patient maintained full ankle joint mobility. Magnetic resonance imaging findings revealed diffusely bulky Achilles tendons with specific imaging characteristics consistent with xanthomatosis. Further evaluation of the lipid profile confirmed hypercholesterolemia and hyperlipidemia. Given the absence of pain or movement restrictions, the patient was managed conservatively with monitoring and treatment for his lipid abnormalities.
Conclusion: This case of bilateral xanthomatosis of the Achilles tendon highlights its rarity and the importance of imaging techniques in diagnosis. Early recognition is critical, as it serves as a potential indicator of underlying hyperlipidemia, necessitating appropriate management to prevent complications. In this instance, conservative treatment was deemed suitable due to the absence of significant symptoms, emphasizing the need for ongoing observation and treatment for the identified lipid disorder.
Keywords: Xanthoma; conservative management; familial hypercholesterolemia; pseudo-tumor; tendon Achilles.
Copyright: © Indian Orthopaedic Research Group.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: Nil
Figures
References
-
- Tsouli SG, Kiortsis DN, Argyropoulou MI, Mikhailidis DP, Elisaf MS. Pathogenesis, detection and treatment of Achilles tendon xanthomas. Eur J Clin Invest. 2005;35:236–44. - PubMed
-
- Rekha A, Rai DK. Tendon xanthomas. Foot (Edinb) 2010;20:85–6. - PubMed
-
- Khot R, Nagpure K. Familial hypercholesterolemia with different types of xanthomas. J Assoc Physicians India. 2018;66:86. - PubMed
-
- Fahey JJ, Stark HH, Donovan WF, Drennan DB. Xanthoma of the Achilles tendon. Seven cases with familial hyperbetalipoproteinemia. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1973;55:1197–211. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous