Helicobacter pylori and Atrial Fibrillation: Insights into Their Inter-Relationship
- PMID: 40351687
- PMCID: PMC12059773
- DOI: 10.31083/RCM26911
Helicobacter pylori and Atrial Fibrillation: Insights into Their Inter-Relationship
Abstract
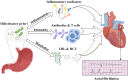
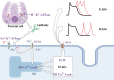
Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infection and atrial fibrillation (AF) are prevalent global health concerns that significantly impact societal and economic well-being. This study explored the potential associations between H. pylori infection and the incidence and progression of AF. Emerging research suggests that H. pylori may influence AF through various pathways, including systemic inflammation, metabolic disturbances, immune responses, and changes in the gut microbiota. These pathways provide a novel perspective on the etiology of AF, suggesting that chronic H. pylori infection could exacerbate or even initiate the arrhythmic events typical of AF. Current evidence, while preliminary, points to significant correlations, particularly through changes in markers such as C-reactive protein (CRP) and lipid metabolism, which are heightened in individuals with active H. pylori infection. However, the exact mechanisms and causal nature of this relationship remain elusive, with studies showing conflicting results. This inconsistency underscores the need for more comprehensive and rigorously designed clinical and experimental research to elucidate fully the interactions between H. pylori infection and AF. Understanding these connections is crucial for developing innovative treatments and management strategies targeting microbial influences in AF patients. Future research should focus on defining the role of H. pylori eradication in the clinical management of AF assessing its impact on disease progression and patient outcomes.
Keywords: Helicobacter pylori; atrial fibrillation; gut microbiota; inflammation.
Copyright: © 2025 The Author(s). Published by IMR Press.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Is there a link between atrial fibrillation and Helicobacter pylori infections?Minerva Gastroenterol (Torino). 2024 Jun;70(2):177-180. doi: 10.23736/S2724-5985.23.03323-5. Epub 2023 Feb 6. Minerva Gastroenterol (Torino). 2024. PMID: 36745411
-
Frequency of helicobacter pylori seropositivity and C-reactive protein increase in atrial fibrillation in patients undergoing coronary angiography.Am J Cardiol. 2008 Mar 15;101(6):848-51. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2007.09.118. Epub 2008 Jan 14. Am J Cardiol. 2008. PMID: 18328851
-
Gut Microbiota: The Missing Link Between Helicobacter pylori Infection and Metabolic Disorders?Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021 Jun 17;12:639856. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.639856. eCollection 2021. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 34220702 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Integrative approaches to atrial fibrillation prevention and management: Leveraging gut health for improved cardiovascular outcomes in the aging population.Curr Probl Cardiol. 2025 Mar;50(3):102952. doi: 10.1016/j.cpcardiol.2024.102952. Epub 2024 Dec 1. Curr Probl Cardiol. 2025. PMID: 39626858 Review.
-
Interactions between Helicobacter pylori infection and host metabolic homeostasis: A comprehensive review.Helicobacter. 2023 Dec;28(6):e13030. doi: 10.1111/hel.13030. Epub 2023 Oct 23. Helicobacter. 2023. PMID: 37871913 Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

