Predictive Value of the White Blood Cells Count for the Prognosis of Hospitalized Patients with Acute Aortic Dissection
- PMID: 40351700
- PMCID: PMC12059737
- DOI: 10.31083/RCM26347
Predictive Value of the White Blood Cells Count for the Prognosis of Hospitalized Patients with Acute Aortic Dissection
Abstract
Objective: Our study evaluated the prognostic significance of white blood cells (WBC) count and WBC subsets in relation to the risk of mortality in acute aortic dissection (AAD) patients during their hospital stay.
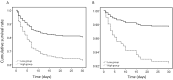
Methods: We included 833 patients with AAD in this retrospective study. The primary outcome was in-hospital mortality. Cox regression analysis was employed to determine the independent risk factors for mortality in patients with AAD. Amidst the low- and high-WBC groups, we use Kaplan‒Meier survival analysis to compare the cumulative survival rates of patients with AAD.
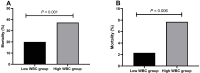
Results: Within 342 patients with type A AAD, patients belonging to the high-WBC group exhibited a notably higher mortality rate compared to patients in the low-WBC group. Kaplan-Meier analysis exhibited that the patients in high-WBC patients had a significantly higher mortality rate. Multivariable Cox regression analysis demonstrated that an elevated WBC was an independent impact factor of in-hospital mortality of patients with type A AAD (hazard ratio, 2.01; 95% confidence interval (CI): 1.24 to 3.27; p = 0.005). Corresponding outcomes were witnessed in 491 patients with type B AAD.
Conclusions: An elevated WBC count was strongly correlated with an elevated risk of mortality in hospitalized patients afflicted with either type A or type B AAD.
Keywords: acute aortic dissection; in-hospital mortality; predictive value; white blood cells count.
Copyright: © 2025 The Author(s). Published by IMR Press.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Isselbacher EM, Preventza O, Hamilton Black J, 3rd, Augoustides JG, Beck AW, Bolen MA, et al. 2022 ACC/AHA Guideline for the Diagnosis and Management of Aortic Disease: A Report of the American Heart Association/American College of Cardiology Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation . 2022;146:e334–e482. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000001106. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

