Exosome-Based Therapeutics in Dermatology
- PMID: 40351703
- PMCID: PMC12062580
- DOI: 10.34133/bmr.0148
Exosome-Based Therapeutics in Dermatology
Abstract
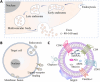
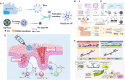
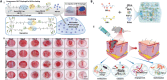
Exosomes (Exos) are tiny extracellular vesicles containing a variety of active biomolecules that play important parts in intercellular communication and influence the functions of target cells. The potential of Exos in the treatment of dermatological diseases has recently been well appreciated. This review highlights the constituents, function, and delivery of Exos, with a particular focus on their applications in skin therapy. Firstly, we offer a concise overview of the biochemical properties of Exos, including their sources, structures, and internal constituents. Subsequently, the biomedical functions of Exos and the latest advances in the extraction and purification of Exos are summarized. We further discuss the modes of delivery of Exos and underscore the potential of biomaterials in this regard. Finally, we summarize the application of Exo-aided therapy in dermatology. Overall, the objective of this review is to provide a comprehensive perspective on the applications and recent advancements of Exo-based approaches in treating skin diseases, with the intention of guiding future research efforts.
Copyright © 2025 Lanjie Lei et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Li H, Zhang J, Tan M, Yin Y, Song Y, Zhao Y, Yan L, Li N, Zhang X, Bai J, et al. Exosomes based strategies for cardiovascular diseases: Opportunities and challenges. Biomaterials. 2024;308:122544. - PubMed
-
- Pan W, Chen H, Wang A, Wang F, Zhang X. Challenges and strategies: Scalable and efficient production of mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes for cell-free therapy. Life Sci. 2023;319: Article 121524. - PubMed
-
- Huang S, Ji X, Jackson KK, Lubman DM, Ard MB, Bruce TF, Marcus RK. Rapid separation of blood plasma exosomes from low-density lipoproteins via a hydrophobic interaction chromatography method on a polyester capillary-channeled polymer fiber phase. Anal Chim Acta. 2021;1167: Article 338578. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

