Effect of Celastrus paniculatus on Alcohol-Elicited Conditioned Place Preference and Alcohol Withdrawal-Induced Anxiety in Mice
- PMID: 40351978
- PMCID: PMC12063638
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.81962
Effect of Celastrus paniculatus on Alcohol-Elicited Conditioned Place Preference and Alcohol Withdrawal-Induced Anxiety in Mice
Abstract
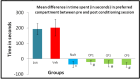
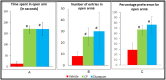
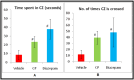
Background Celastrus paniculatus (CP), an Indian medicinal plant, is hypothesized to be effective in alcohol use disorder (AUD) based on its medicinal properties useful in CNS disorders as per ancient Ayurveda literature. Hence, it was tested in animal models of AUD. Methodology The study was conducted in Swiss albino mice (n=144) of either sex after obtaining Institutional Animal Ethics Committee permission. Three doses of seed oil of CP (CP1: 140, CP2: 280 and CP3: 560 mg/kg) were administered orally in milk (vehicle for CP). A conditioned place preference (CPP) model was used to study the effect of CP on alcohol dependence. Elevated plus maze (EPM) and open field test (OFT) were used to study its effect on alcohol withdrawal-induced anxiety. Naltrexone and diazepam were used as positive controls. Results The results in all the CP groups (CP1 (337.88±20.66s, p<0.05); CP2 (322.38±17.61s, p<0.05) and CP3 (315.50±4.24s) as evaluated by the time spent in alcohol paired compartment in CPP) showed better protection against alcohol dependence as compared to the vehicle (552.63±27.47s, p<0.05). The values in all the CP groups were comparable to the naltrexone group. In the EPM test, the CP3 group showed significantly increased time spent (170.63±19.75s) in the open arm (vs the vehicle control, 12.75±11.03s, p<0.05). Also in OFT, longer time was spent in the central zone by mice in the CP3 group (23.25±6.19s vs.8.50±5.48s in the vehicle group, p<0.05). The results of the CP3 group were comparable to diazepam in EPM and OFT experiments. Conclusion Celastrus paniculatus seed oil showed a dose-dependent effect in the CPP model of alcohol dependence in mice. The highest dose of CP also prevented alcohol withdrawal-induced anxiety.
Keywords: anxiety; dependence; diazepam; intermittent access; naltrexone.
Copyright © 2025, Satam et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Human subjects: All authors have confirmed that this study did not involve human participants or tissue. Animal subjects: Institutional Animal Ethics Committee, King Edward Memorial Hospital and Seth Gordhandas Sunderdas Medical College, Mumbai Issued protocol number AEC/02/2014. Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: The study was funded by the Ministry of AYUSH, Government of India. (Z.28015/236/2015-HPC(EMR)-AYUSH-A). Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures
References
-
- Global status report on alcohol and health. 2014. https://www.who.int/substance_abuse/publications/alcohol_2014/en/ https://www.who.int/substance_abuse/publications/alcohol_2014/en/
-
- Gururaj G, Varghese M, Benegal V, Rao GN. Bengaluru, National Institute of Mental Health and Neuro Sciences, NIMHANS Publication No. 128. Bengaluru: National Institute of Mental Health and Neuro Sciences; 2016. National Mental Health Survey of India, 2015-16: Summary, NIMHANS Publication No. 128.
-
- Naltrexone, a relapse prevention maintenance treatment of alcohol dependence: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Streeton C, Whelan G. Alcohol Alcohol. 2001;36:544–552. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
