High-resistance inspiratory muscle strength training: a promising strategy for improving vascular health in chronic kidney disease
- PMID: 40352145
- PMCID: PMC12061950
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2025.1582777
High-resistance inspiratory muscle strength training: a promising strategy for improving vascular health in chronic kidney disease
Abstract
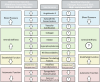
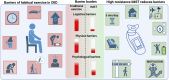
Patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) demonstrate accelerated vascular aging which contributes to an increased risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD). Impaired vascular health in CKD is characterized by both functional and structural alterations to the vasculature including hypertension, arterial stiffness, vascular endothelial dysfunction, and autonomic dysfunction. These detriments persist despite pharmacological intervention. Habitual aerobic exercise can be protective of vascular health; however, the feasibility in patients with CKD is low due to numerous barriers to exercise. In this perspective we emphasize the need for novel and non-pharmacological strategies that can rescue vascular health and reduce the development of CVD in patients with CKD, explain the unique barriers to aerobic exercise in CKD, present a novel physical training intervention-high-resistance inspiratory muscle strength training (IMST) that addresses the barriers to exercise, and provide our opinion on why this lifestyle intervention may be particularly efficacious for patients with CKD.
Keywords: chronic kidney disease; exercise training; inspiratory; lifestyle interventions; vascular health.
Copyright © 2025 Lapierre-Nguyen, Buffington, Chonchol and Nowak.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Becker G. J., Wheeler D. C., De Zeeuw D., Fujita T., Furth S. L., Holdaas H., et al. (2012). Kidney disease: improving global outcomes (KDIGO) blood pressure work group. KDIGO clinical practice guideline for the management of blood pressure in chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. Suppl. 2 (5), 337–414.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

