Age- and sex-specific reference values for CT-based low skeletal muscle quantity and quality in healthy living kidney donors
- PMID: 40352149
- PMCID: PMC12061965
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2025.1566463
Age- and sex-specific reference values for CT-based low skeletal muscle quantity and quality in healthy living kidney donors
Abstract
Background: Computed tomography (CT) imaging is a useful tool for assessing skeletal muscle mass and quality. The present study aimed to determine age- and sex-specific reference values for CT-based skeletal muscle markers in a healthy population, and to correlate them with serum creatinine and 24-h urinary creatinine excretion (24h-UCE).
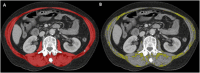
Methods: Skeletal muscle index (SMI) - a marker of muscle mass/quantity - and skeletal muscle radiation attenuation (SMRA) and intermuscular adipose tissue index (IMATI) - markers of muscle quality/myosteatosis - were determined using a deep-learning-based method from axial CT images at the level of the 3rd lumbar vertebra in living kidney donors assessed between 01/2005 and 05/2023. Age- and sex-specific reference values were determined by the 5th percentile, and correlation was tested with the Pearson correlation coefficient.
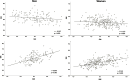
Results: CT scans of 394 healthy individuals were included. The mean age was 53 years (SD 12), mean BMI was 25.2 kg/m2 (SD 3.9), and 130 patients (33%) were male. The reference values for low skeletal muscle mass (SMI) in males were 43.7 cm2/m2 (20-39 years), 44.9 cm2/m2 (40-59 years), and 39.7 cm2/m2 (≥60 years). In females, the corresponding values were 33.8 cm2/m2 (20-39 years), 34.8 cm2/m2 (40-59 years), and 31.2 cm2/m2 (≥60 years). SMI showed a moderate correlation with serum creatinine (r = 0.452, p < 0.001) but a weak correlation with 24h-UCE (r = 0.188, p = 0.003). Correlations were all weak for SMRA (creatinine: r = 0.220, p < 0.001; 24h-UCE: r = 0.177, p = 0.006) and IMATI (creatinine: r = -0.101, p = 0.054; 24h-UCE, r = -0.108, p = 0.093).
Conclusion: The age- and sex-specific reference values reported here could be used in clinical practice and future studies to identify patients at risk of muscle decline.
Keywords: computed tomography; living kidney donor; muscle mass; muscle quality; myosteatosis.
Copyright © 2025 Martin, Dolce, Hübner, Zingg, Fuks, Venetz, Maier, Matter and Becce.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

