Exploring the role of polysaccharides in mitigating organ damage caused by pesticide-induced toxicity: A systematic review and meta-analysis of in vivo studies
- PMID: 40352195
- PMCID: PMC12059844
- DOI: 10.52225/narra.v5i1.1553
Exploring the role of polysaccharides in mitigating organ damage caused by pesticide-induced toxicity: A systematic review and meta-analysis of in vivo studies
Abstract
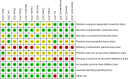
Although polysaccharides have demonstrated potential in alleviating dysbiosis, the overall impact of polysaccharides on minimizing oxidative stress and organ damage in vivo has not been thoroughly investigated. The aim of this study was to investigate the comprehensive effects of polysaccharides in mitigating pesticide toxicity in animal studies, focusing on biomarkers related to oxidative stress, antioxidant activity, kidney injury, lipid profiles, liver function, and the preservation of liver and kidney weights. A systematic search was conducted across nine indexed databases, including PubMed, Cochrane CENTRAL, Taylor & Francis, Scopus, Sage, EBSCO, ProQuest, ScienceDirect, and Google Scholar. Rayyan.ai was used to screen in vivo studies that met the predefined inclusion and exclusion criteria. The quality of the selected in vivo studies was evaluated using SYRCLE's Risk of Bias tool, specifically designed for animal studies. Thirteen randomized animal studies, comprising 330 mice and rats, were included in the analysis. The findings revealed that polysaccharides significantly increased antioxidant levels, including catalase (CAT) (p<0.00001), superoxide dismutase (SOD) (p<0.00001), glutathione peroxidase (GPx) (p<0.00001), and reduced glutathione (GSH) (p<0.00001). Polysaccharides also significantly reduced oxidative stress markers, such as malondialdehyde (MDA) (p<0.00001) and nitric oxide (NO) (p<0.0001), as well as kidney injury biomarkers, including serum creatinine (p<0.00001) and urea (p<0.00001). Additionally, improvements in lipid profiles were observed, with significant reductions in triglycerides (TG) (p=0.04) and total cholesterol (TC) (p<0.00001). However, there were no significant differences in high-density lipoprotein (HDL) (p=0.28) and low-density lipoprotein (LDL) (p=0.32) levels. Polysaccharides significantly alleviate liver biomarkers, including aspartate transaminase (AST) (p<0.0001), alanine transaminase (ALT) (p<0.005), and alkaline phosphatase (ALP) (p<0.0001). Polysaccharides also contributed to the maintenance of liver weight (p=0.009), although no significant differences were observed in kidney weights (p=0.81). The study highlights that polysaccharides exert significant effects in enhancing antioxidant levels, reducing oxidative stress and organ damage biomarkers, and preserving liver weights.
Keywords: Dysbiosis; gut microbiota; oxidative stress; pesticide; polysaccharides.
© 2025 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
All the authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures








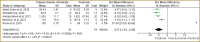









Similar articles
-
Antioxidants for female subfertility.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013 Aug 5;(8):CD007807. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007807.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Jul 28;7:CD007807. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007807.pub3. PMID: 23913583 Updated.
-
Study on the modulation of kidney and liver function of rats with diabetic nephropathy by Huidouba through metabolomics.J Ethnopharmacol. 2025 Jul 24;351:120136. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2025.120136. Epub 2025 Jun 11. J Ethnopharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40513925
-
Antioxidants for male subfertility.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014;(12):CD007411. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007411.pub3. Epub 2014 Dec 15. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Mar 14;3:CD007411. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007411.pub4. PMID: 25504418 Updated.
-
Zinc sulfate improves insulin resistance, oxidative stress and apoptosis in liver tissues of PCOS rats through the NF-κB pathway.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025 Jun 6;16:1569866. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1569866. eCollection 2025. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40547527 Free PMC article.
-
Manganese mitigates atrazine-induced oxidative stress and hepatorenal toxicity: insights from network pharmacology and in vivo experimentation.BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2025 Jul 15;26(1):133. doi: 10.1186/s40360-025-00966-4. BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2025. PMID: 40665419 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Suratman S, Suhartono S. Pesticides exposure and thyroid hormone levels among agricultural workers and pesticide applicators: A systematic review. JKL 2022;14(3):178–192.
-
- Elshamy R, Hassan A, El-Naggar S, et al. . Oxidative stress indices of organophosphates pesticides among agricultural workers at Mit-Ghamr District, Egypt. ZUMJ 2019;25(2):187–197.
-
- Chang JCJ, Yang HY. Epidemiology of chronic kidney disease of undetermined aetiology in Taiwanese farmers: A cross-sectional study from Changhua community-based integrated screening programme. Occup Environ Med 2021;78(12):849–858. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
