Synergistic mechanism of Phyllanthus emblica extract and tetracycline against multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii
- PMID: 40352204
- PMCID: PMC12059877
- DOI: 10.52225/narra.v5i1.1939
Synergistic mechanism of Phyllanthus emblica extract and tetracycline against multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii
Abstract
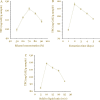
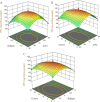
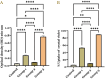
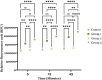
The rising incidence of multidrug-resistant (MDR) Acinetobacter baumannii infections underscores the urgent need for novel antimicrobial strategies. The aim of this study was to investigate the synergistic effects between a polyphenol-rich extract from Phyllanthus emblica fruit and tetracycline against MDR A. baumannii strains. The extraction process was optimized using the Box-Behnken design approach to maximize the total phenolic content (TPC) of the P. emblica extract. Key variables, including ethanol concentration, extraction time, and solid-to-liquid ratio (w/v), were determined through single-factor experiments. The antimicrobial activity of the extract, both alone and in combination with tetracycline, was evaluated against A. baumannii. Mechanistic studies focusing on bacterial lysis and efflux pump inhibition were conducted to assess the extract's effects and its combined potential with tetracycline. The Box-Behnken design successfully optimized the extraction conditions, yielding the highest TPC at 68.92% ethanol concentration, 1.85 days of extraction time, and a 1:9.58 w/v ratio. The predicted and experimentally verified TPC values of the extract were 129.19 and 130.76 ± 2.46 mg GAE/g samples, respectively, with no significant difference (p > 0.05). The extract contained several phenolic compounds identified using liquid chromatography-high-resolution mass spectrometry (LC-HRMS). It exhibited antimicrobial activity against MDR Acinetobacter baumannii, either alone or in combination with tetracycline. The combination demonstrated a synergistic effect against MDR A. baumannii, with a fractional inhibitory concentration index (FICI) of 0.37. Moreover, the combination showed superior bacteriolytic effects against MDR A. baumannii cells, as evidenced by increased release of nucleic acid components and membrane destabilization, compared to the extract or tetracycline alone (p < 0.0001 for all comparisons). Additionally, the combination significantly enhanced the efflux pump inhibition effect compared to the extract or tetracycline alone (p < 0.05 for both). These findings support the potential use of polyphenol-rich P. emblica extracts as adjuncts to conventional antibiotics in treating drug-resistant bacterial infections.
Keywords: Acinetobacter baumannii; Phyllanthus emblica; antimicrobial activity; multidrug-resistant; total phenolic content.
© 2025 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
All the authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Synergistic effects of ethnomedicinal plants of Apocynaceae family and antibiotics against clinical isolates of Acinetobacter baumannii.Asian Pac J Trop Med. 2014 Jun;7(6):456-61. doi: 10.1016/S1995-7645(14)60074-2. Asian Pac J Trop Med. 2014. PMID: 25066394
-
Isolation and characterization of antimicrobial compounds in plant extracts against multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii.PLoS One. 2013 Apr 22;8(4):e61594. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0061594. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23630600 Free PMC article.
-
Fruit Extract and Phenolic Compounds of Phyllanthus emblica Fruits as Bioactivity Enhancer of Chloramphenicol Against Bacterial Species.Plant Foods Hum Nutr. 2024 Sep;79(3):656-661. doi: 10.1007/s11130-024-01206-6. Epub 2024 Jul 1. Plant Foods Hum Nutr. 2024. PMID: 38951374
-
Types and Mechanisms of Efflux Pump Systems and the Potential of Efflux Pump Inhibitors in the Restoration of Antimicrobial Susceptibility, with a Special Reference to Acinetobacter baumannii.Pathogens. 2024 Feb 23;13(3):197. doi: 10.3390/pathogens13030197. Pathogens. 2024. PMID: 38535540 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Deciphering the impact of Acinetobacter baumannii on human health, and exploration of natural compounds as efflux pump inhibitors to treat multidrug resistance.J Med Microbiol. 2024 Aug;73(8). doi: 10.1099/jmm.0.001867. J Med Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39212030 Review.
References
-
- de Santana CF, da Silva Cirino IC, de Souza LIO, et al. . Antimicrobial and cytotoxic effects of Lippia alba essential oil on multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii clinical isolates. S Afr J Bot 2024;175:479–485.
-
- Havill NL, Samuels M, Poudyal A, et al. . Elimination of an outbreak of carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii in a burn unit. Am J Infect Control 2025;53(1):160–162. - PubMed
-
- Bustamante V, Palavecino CE. Effect of photodynamic therapy on multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii: A scoping review. Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther 2023;43:103709. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
