Diagnostic accuracy of preoperative ultrasonography-guided fine-needle aspiration biopsy in distinguishing malignancy in large thyroid nodules: A systematic review, meta-analysis, and meta-regression
- PMID: 40352242
- PMCID: PMC12059824
- DOI: 10.52225/narra.v5i1.1120
Diagnostic accuracy of preoperative ultrasonography-guided fine-needle aspiration biopsy in distinguishing malignancy in large thyroid nodules: A systematic review, meta-analysis, and meta-regression
Abstract
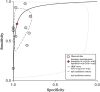
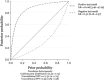
Controversy persists regarding the effectiveness of ultrasonography-guided fine-needle aspiration biopsy (US-FNAB) in distinguishing malignancies in large thyroid nodules. The prevailing belief that larger thyroid nodules inherently pose a higher risk of malignancy has led to a common practice of suggesting thyroidectomy for large thyroid nodules. Herein, the aim of this study was to assess the diagnostic accuracy of preoperative US-FNAB for distinguishing malignancy in large thyroid nodules. A search for published records was carried out on October 20, 2023, utilizing the search feature available on PubMed, Scopus, Embase, and Google Scholar. Patients with large thyroid nodules (3 cm or larger) who underwent preoperative US-FNAB and postoperative histopathological tests were included. Related outcomes, including false positive, false negative, true negative, true positive, specificity, and sensitivity, were extracted from each study. Pooled specificity and sensitivity were estimated, and the summarized receiver operating characteristic (sROC) curve, along with the summarized area under the curve (sAUC), was calculated. Out of 133 articles identified across four databases, ten studies with a total sample of 2752 patients were included. The overall diagnostic sensitivity was 72% (95%CI: 50-86%; p=0.00) and specificity was 96% (95%CI: 87-90%; p=0.00). The positive predictive value (PPV) and negative predictive value (NPV) were 93% (95%CI: 89-98%) and 75% (95%CI: 72-79%), respectively. sAUC was 93%, suggesting the diagnostic tool is accurate. Meta-regression analysis revealed that factors such as the number of samples, country (high-income vs upper-middle income), demographic characteristics (age and sex), and different thyroid size cut-off values did not significantly impact the sensitivity or specificity of US-FNAB. In conclusion, the present study confirms the reliability of US-FNAB in distinguishing malignancy in large thyroid nodules, emphasizing its role in reducing unnecessary thyroidectomy by identifying high-risk patients and challenging the conventional practice of routine thyroidectomy for large thyroid nodules.
Keywords: Large thyroid nodule; accuracy; fine-needle aspiration; histopathology; review.
© 2025 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
All the authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Assessing the Diagnostic Accuracy of TI-RADS in Pediatric Thyroid Nodules: A Multi-institutional Review.J Pediatr Surg. 2025 Jan;60(1):161924. doi: 10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2024.161924. Epub 2024 Sep 13. J Pediatr Surg. 2025. PMID: 39358076
-
The Role of Core Needle Biopsy for Thyroid Nodules with Initially Indeterminate Results on Previous Fine-Needle Aspiration: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2017 Jul;38(7):1421-1426. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A5182. Epub 2017 May 4. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2017. PMID: 28473343 Free PMC article.
-
Qualitative elastography can replace thyroid nodule fine-needle aspiration in patients with soft thyroid nodules. A systematic review and meta-analysis.Eur J Radiol. 2015 Apr;84(4):652-61. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2015.01.003. Epub 2015 Jan 16. Eur J Radiol. 2015. PMID: 25638577
-
Diagnostic Performance of Ultrasound vs Ultrasound-Guided FNAC in Thyroid Nodules: Data From the ElaTION Trial.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2025 Jun 17;110(7):1997-2006. doi: 10.1210/clinem/dgae682. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2025. PMID: 39359050 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Ultrasound is helpful to differentiate Bethesda class III thyroid nodules: A PRISMA-compliant systematic review and meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2017 Apr;96(16):e6564. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000006564. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017. PMID: 28422844 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brito JP, Yarur AJ, Prokop LJ, et al. . Prevalence of thyroid cancer in multinodular goiter versus single nodule: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Thyroid 2013;23(4):449–455. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
