Molecular design and performance of emissive amide-containing compounds as corrosion inhibitors: synthesis, electrochemical evaluation, DFT calculations and molecular dynamics simulations
- PMID: 40352398
- PMCID: PMC12063569
- DOI: 10.1039/d5ra00978b
Molecular design and performance of emissive amide-containing compounds as corrosion inhibitors: synthesis, electrochemical evaluation, DFT calculations and molecular dynamics simulations
Abstract
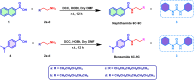
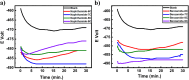
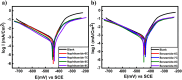
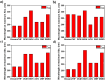
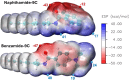
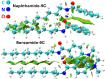
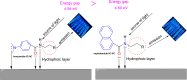
Corrosion presents a significant challenge across various industries, resulting in considerable economic losses and safety risks. Organic compounds that contain aryl moieties and hetero atoms like nitrogen and oxygen have potential applications as efficient inhibitors and coating layers for the surface of metals. Herein, we investigate the corrosion inhibition of mild steel in 1.0 M H2SO4 using newly synthesized amide-containing compounds with naphthalene (naphthamide 6C-9C) or benzene (benzamide 6C-9C) structures. Characterization of these inhibitors via IR and NMR spectroscopy confirmed their chemical structures. Electrochemical analyses, including open circuit potential and potentiodynamic polarization tests, showed that these compounds significantly reduce the corrosion rate of mild steel. They achieved inhibition efficiencies up to 80% at optimal concentrations. The enhanced performance of these inhibitors is linked to their greater molecular weight and longer alkyl chains, which improve adsorption and surface coverage. Photophysical investigations revealed notable solvatochromic effects and red shifts in polar solvents, indicating strong interactions with the environment. Density Functional Theory (DFT) calculations provided further insights into the molecular structure, electronic distributions, and adsorption behavior, confirming the higher efficiency of series naphthamide 6C-9C compared to benzamide 6C-9C. Moreover, molecular Dynamics (MD) simulations corroborated the formation of stable protective layers on the metal surface. From the DFT calculations it is evidently that naphthamide 9C exhibited a smaller HOMO-LUMO energy gap compared to compound benzamide 9C, indicating higher reactivity and greater inhibitory efficiency. The integration of experimental and theoretical findings confirms that amide-containing naphthalene and benzene derivatives are highly effective corrosion inhibitors, suitable for industrial applications.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors state that there are no conflicts to declare.
Figures




References
-
- Imran M. M. H. Jamaludin S. Mohamad Ayob A. F. A critical review of machine learning algorithms in maritime, offshore, and oil & gas corrosion research: A comprehensive analysis of ANN and RF models. Ocean Eng. 2024;295:116796. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2024.116796. - DOI
-
- Sharma A. Kaur J. Saxena A. Anti-corrosive Properties of Synthetic Organic Compounds: A Review. J. Bio- Tribo-Corros. 2024;10:80. doi: 10.1007/s40735-024-00884-8. - DOI
-
- Guo L. et al., Electrochemical and surface investigations of N, S codoped carbon dots as effective corrosion inhibitor for mild steel in acidic solution. Colloids Surf., A. 2024;702:135062. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfa.2024.135062. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

