Design and Characterization of Peptide-Conjugated Solid Lipid Nanoparticles for Targeted MRI and SPECT Imaging of Breast Tumors
- PMID: 40352495
- PMCID: PMC12059910
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.4c10153
Design and Characterization of Peptide-Conjugated Solid Lipid Nanoparticles for Targeted MRI and SPECT Imaging of Breast Tumors
Abstract
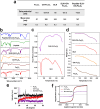
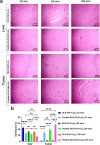
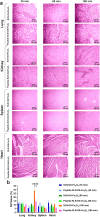
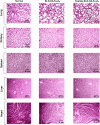
Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) presents significant challenges due to its aggressive behavior and lack of targeted treatments. High-resolution imaging techniques and targeted nanoparticles offer potential solutions for early detection and monitoring of TNBC. In this study, we developed and characterized solid lipid nanoparticles (SLNs) conjugated with a C-peptide derived from endostatin to target integrin αvβ3, overexpressed in TNBC. These SLNs were loaded with superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPIONs) for enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and radiolabeled with technetium-99m (99mTc) for single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT), enabling dual-modality imaging. Extensive characterization of the nanoparticles was performed utilizing a variety of advanced techniques, including dynamic light scattering (DLS), differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), thermogravimetric analysis (TGA), X-ray diffraction (XRD), vibrating sample magnetometry (VSM), field-emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM), and atomic force microscopy (AFM). This comprehensive analysis validated the successful synthesis and functionalization of the nanoparticles, along with their remarkable magnetic properties, while also revealing their distinct spherical morphology, optimal size, uniform distribution, and colloidal stability. The conjugation of C-peptide significantly enhanced the targeting efficiency in vitro, as evidenced by the MTT and receptor-binding assays in 4T1 cells using flow cytometry and MRI. In vivo studies using a 4T1 murine model demonstrated that peptide-conjugated SLNs accumulated in tumor tissues, providing superior contrast in MRI and enhanced tumor-specific localization in SPECT imaging. Biodistribution analysis confirmed reduced off-target accumulation, particularly in the liver, compared to nontargeted formulations. Collectively, C-peptide-conjugated SLNs provide a promising dual-modality imaging platform for TNBC, offering improved diagnostic accuracy and tumor targeting.
© 2025 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Development and application of dual-modality tumor-targeting SPIONs for precision breast cancer imaging.Biomater Adv. 2025 Jul;172:214236. doi: 10.1016/j.bioadv.2025.214236. Epub 2025 Feb 19. Biomater Adv. 2025. PMID: 40010023
-
Advancing triple-negative breast cancer treatment through peptide decorated solid lipid nanoparticles for paclitaxel delivery.Sci Rep. 2025 Feb 19;15(1):6043. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-90107-y. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39972039 Free PMC article.
-
68Ga-radiolabeled bombesin-conjugated to trimethyl chitosan-coated superparamagnetic nanoparticles for molecular imaging: preparation, characterization and biological evaluation.Int J Nanomedicine. 2019 Apr 10;14:2591-2605. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S195223. eCollection 2019. Int J Nanomedicine. 2019. PMID: 31040674 Free PMC article.
-
99mTc-labeled superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for multimodality SPECT/MRI of sentinel lymph nodes.J Nucl Med. 2012 Mar;53(3):459-63. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.111.092437. Epub 2012 Feb 9. J Nucl Med. 2012. PMID: 22323777
-
Radiolabeled Iron Oxide Nanoparticles as Dual Modality Contrast Agents in SPECT/MRI and PET/MRI.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2023 Jan 27;13(3):503. doi: 10.3390/nano13030503. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36770463 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Liu C.; Zhao Z.; Gao R.; Zhang X.; Sun Y.; Wu J.; Liu J.; Chen C. Matrix metalloproteinase-2-responsive surface-changeable liposomes decorated by multifunctional peptides to overcome the drug resistance of triple-negative breast cancer through enhanced targeting and penetrability. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2022, 8 (7), 2979–2994. 10.1021/acsbiomaterials.2c00295. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Zheng X.-C.; Ren W.; Zhang S.; Zhong T.; Duan X.-C.; Yin Y.-F.; Xu M.-Q.; Hao Y.-L.; Li Z.-T.; Li H. The theranostic efficiency of tumor-specific, pH-responsive, peptide-modified, liposome-containing paclitaxel and superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 1495–1504. 10.2147/IJN.S157082. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Mohajeri M.; Salehi P.; Heidari B.; Rafati H.; Asghari S. M.; Behboudi H.; Iranpour P. PEGylated Pemetrexed and PolyNIPAM Decorated Gold Nanoparticles: A Biocompatible and Highly Stable CT Contrast Agent for Cancer Imaging. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2024, 7 (9), 5977–5991. 10.1021/acsabm.4c00563. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
