Pulmonary Injury Induced via Metal-Organic Frameworks (MOFs): ROS Generation and Inflammatory Responses Mediated by HKUST-1
- PMID: 40352508
- PMCID: PMC12059943
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.5c00670
Pulmonary Injury Induced via Metal-Organic Frameworks (MOFs): ROS Generation and Inflammatory Responses Mediated by HKUST-1
Abstract
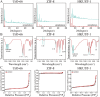
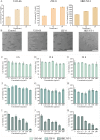
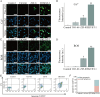
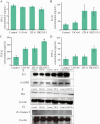
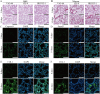
Owing to their tunable structural and functional characteristics, innovative materials known as metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) have become a research focus in scientific communities, demonstrating significant potential across biomedical applications, including targeted drug delivery, tumor detection technologies, and sophisticated medical imaging diagnostics. Despite the growing interest in their therapeutic potential, the systemic and pulmonary toxicity of MOFs remains inadequately explored, particularly about the long-term effects of metal ion release during degradation. This study investigates the pulmonary toxicity of three widely studied MOFs, UiO-66, ZIF-8, and HKUST-1, focusing on the mechanisms of oxidative stress and inflammation. The in vitro and in vivo assays demonstrated that HKUST-1 induced significant cytotoxicity, oxidative stress, and apoptosis in lung cells, primarily due to its copper content. In contrast, UiO-66 and ZIF-8 exhibited minimal toxicity. These results emphasize the essential requirement for understanding the toxicological profiles of MOFs and highlight the necessity of modifying their structure to enhance safety for biomedical applications.
© 2025 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures

References
-
- Mane P. V.; Rego R. M.; Yap P. L.; Losic D.; Kurkuri M. D. Unveiling Cutting-Edge Advances in High Surface Area Porous Materials for the Efficient Removal of Toxic Metal Ions from Water. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2024, 146, 101314.10.1016/j.pmatsci.2024.101314. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
