Time to Initiation of Hepatitis B Treatment is Reduced With the Use of the Xpert HBV Viral Load Kit
- PMID: 40352629
- PMCID: PMC12063097
- DOI: 10.1093/ofid/ofaf238
Time to Initiation of Hepatitis B Treatment is Reduced With the Use of the Xpert HBV Viral Load Kit
Abstract
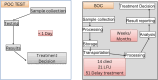
Timely initiation of hepatitis B virus treatment is essential for improving prognosis and outcomes. In Ethiopia, the use of the Xpert hepatitis B virus viral load kit significantly shortened the turnaround time compared to standard laboratory methods. By reducing the time to a treatment decision to 1 day, the Xpert kit allowed for quicker treatment initiation at lower costs, potentially saving lives that might otherwise be lost due to treatment delays.
Keywords: antiviral therapy; hepatitis B; point-of-care; resource-limited settings; viral load.
© The Author(s) 2025. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Infectious Diseases Society of America.
Conflict of interest statement
Potential conflicts of interest. All authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- World Health Organization . Global hepatitis report 2024: action for access in low-and middle-income countries. Geneva: WHO, 2024.
-
- World Health Organization . Global health sector strategy on viral hepatitis 2016–2021. Towards ending viral hepatitis. Geneva: WHO, 2016.
-
- Lampertico P, Agarwal K, Berg T, et al. EASL 2017 clinical practice guidelines on the management of hepatitis B virus infection. J Hepatol 2017; 67:370–98. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

